Prediabetes and risk for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality based on hypertension status
- PMID: 33437779
- PMCID: PMC7791204
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-1155
Prediabetes and risk for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality based on hypertension status
Abstract
Background: Current recommendations suggest prediabetes testing for overweight or obese adults with at least one cardiovascular risk factor. However, it is important to understand whether testing should be conducted in adults with hypertension regardless of their cardiovascular risk factors.
Methods: Participants from the 1999-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) aged at least 18 years and without diabetes were enrolled in the study. Participants were classified according to their prediabetes and hypertension status and followed up to track cardiovascular and all-cause mortality until December 31, 2015. Cox proportional hazards models were built to estimate the hazard ratios (HRs). Results were stratified by age, sex, ethnicity, body mass index, and cardiovascular disease history.
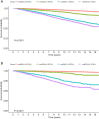
Results: At baseline, 5,011 (14.72%) out of 34,047 participants had combined prediabetes and hypertension. Prediabetes alone was not associated with all-cause or cardiovascular mortality. Hypertension alone was significantly associated with all-cause (HR: 1.30) and cardiovascular (HR: 1.89) mortality, and combined prediabetes and hypertension were significantly associated with all-cause (HR: 1.37) and cardiovascular (HR: 2.11) mortality. Age and ethnicity were significantly associated with combined prediabetes and hypertension and all-cause mortality, where the association was stronger among people aged <60 years (HR: 1.94 vs. 1.22) and White (HR: 1.50 vs. 1.21).
Conclusions: Prediabetes might elevate the risk of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among people with hypertension. This relationship is more evident among younger and White individuals.
Keywords: Prediabetes; all-cause mortality; cardiovascular mortality; hypertension.
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-1155). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2018;71:e13-115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
