A SIQ mathematical model on COVID-19 investigating the lockdown effect
- PMID: 33437896
- PMCID: PMC7789846
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idm.2020.12.010
A SIQ mathematical model on COVID-19 investigating the lockdown effect
Abstract
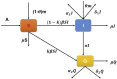
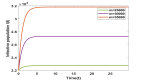
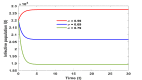
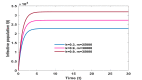
This research paper aims at studying the impact of lockdown on the dynamics of novel Corona Virus Disease (COVID-19) emerged in Wuhan city of China in December 2019. Perceiving the pandemic situation throughout the world, Government of India restricted international passenger traffic through land check post (Liang, 2020) and imposed complete lockdown in the country on 24 March 2020. To study the impact of lockdown on disease dynamics we consider a three-dimensional mathematical model using nonlinear ordinary differential equations. The proposed model has been studied using stability theory of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Basic reproduction ratio is computed and significant parameters responsible to keep basic reproduction ratio less than one are identified. The study reveals that disease vanishes from the system only if complete lockdown is imposed otherwise disease will always persist in the population. However, disease can be kept under control by implementing contact tracing and quarantine measures as well along with lockdown if lockdown is imposed partially.
Keywords: 34D; 34H; 90A; 92B; Persistence; Sensitivity analysis; Stability; System.
© 2021 The Authors. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mathematical modeling of COVID-19 transmission: the roles of intervention strategies and lockdown.Math Biosci Eng. 2020 Sep 10;17(5):5961-5986. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020318. Math Biosci Eng. 2020. PMID: 33120585
-
Impact of lockdown to control over Novel Coronavirus and COVID-19 in India.J Family Med Prim Care. 2020 Oct 30;9(10):5142-5147. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_692_20. eCollection 2020 Oct. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020. PMID: 33409178 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions on the dynamics of novel coronavirus with optimal control analysis with a case study.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2020 Oct;139:110075. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110075. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2020. PMID: 32834618 Free PMC article.
-
A mathematical system of COVID-19 disease model: Existence, uniqueness, numerical and sensitivity analysis.MethodsX. 2023;10:102045. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102045. Epub 2023 Jan 28. MethodsX. 2023. PMID: 36742367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of preventive measures against COVID-19: A systematic review of In Silico modeling studies in indian context.Indian J Public Health. 2020 Jun;64(Supplement):S156-S167. doi: 10.4103/ijph.IJPH_464_20. Indian J Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32496248
Cited by
-
Is Curfew Effective in Limiting SARS-CoV-2 Progression? An Evaluation in France Based on Epidemiokinetic Analyses.J Gen Intern Med. 2021 Sep;36(9):2731-2738. doi: 10.1007/s11606-021-06953-9. Epub 2021 Jun 15. J Gen Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34131877 Free PMC article.
-
An epidemiology-based model for the operational allocation of COVID-19 vaccines: A case study of Thailand.Comput Ind Eng. 2022 May;167:108031. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2022.108031. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Comput Ind Eng. 2022. PMID: 35228772 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 dynamics and immune response: Linking within-host and between-host dynamics.Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2023 Jun 26:113722. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2023.113722. Online ahead of print. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2023. PMID: 38620099 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of human mobility and behavior on disease transmission in a COVID-19 mathematical model.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 27;12(1):10840. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14155-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35760930 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Perception Influence on Vaccination Program on COVID-19 in Chile: A Mathematical Model.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 11;19(4):2022. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19042022. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35206210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aparicio J.P., Hernandez J.C. Preventive treatment of tuberculosis through contact tracing. Contemporary Mathematics. 2006;410:17–20.
-
- Arriola L.M., Hyman J.M. Technical report; 2003. Forward and adjoint sensitivity analysis: With applications in dynamical systems.
-
- Bhola J., Venkateswaran V.R., Koul M. medrxiv; 2020. Corona epidemic in Indian context: Predictive mathematical modelling. 200471753.
-
- Binti H.F.A., Lau C., Nazri H., Ligot D.V., Lee G., Tan C.L. CoronaTracker: World-wide COVID-19 outbreak data analysis and prediction, [preprint] Bull World Health Organ, E-pub. 2020;19:255695.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

