A SIQ mathematical model on COVID-19 investigating the lockdown effect
- PMID: 33437896
- PMCID: PMC7789846
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idm.2020.12.010
A SIQ mathematical model on COVID-19 investigating the lockdown effect
Abstract
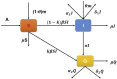
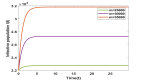
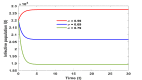
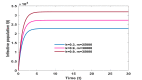
This research paper aims at studying the impact of lockdown on the dynamics of novel Corona Virus Disease (COVID-19) emerged in Wuhan city of China in December 2019. Perceiving the pandemic situation throughout the world, Government of India restricted international passenger traffic through land check post (Liang, 2020) and imposed complete lockdown in the country on 24 March 2020. To study the impact of lockdown on disease dynamics we consider a three-dimensional mathematical model using nonlinear ordinary differential equations. The proposed model has been studied using stability theory of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Basic reproduction ratio is computed and significant parameters responsible to keep basic reproduction ratio less than one are identified. The study reveals that disease vanishes from the system only if complete lockdown is imposed otherwise disease will always persist in the population. However, disease can be kept under control by implementing contact tracing and quarantine measures as well along with lockdown if lockdown is imposed partially.
Keywords: 34D; 34H; 90A; 92B; Persistence; Sensitivity analysis; Stability; System.
© 2021 The Authors. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
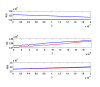
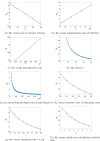
References
-
- Aparicio J.P., Hernandez J.C. Preventive treatment of tuberculosis through contact tracing. Contemporary Mathematics. 2006;410:17–20.
-
- Arriola L.M., Hyman J.M. Technical report; 2003. Forward and adjoint sensitivity analysis: With applications in dynamical systems.
-
- Bhola J., Venkateswaran V.R., Koul M. medrxiv; 2020. Corona epidemic in Indian context: Predictive mathematical modelling. 200471753.
-
- Binti H.F.A., Lau C., Nazri H., Ligot D.V., Lee G., Tan C.L. CoronaTracker: World-wide COVID-19 outbreak data analysis and prediction, [preprint] Bull World Health Organ, E-pub. 2020;19:255695.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

