A plasma metabolomic signature of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy showing taurine and nicotinamide deficiencies
- PMID: 33437983
- PMCID: PMC8033144
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddab013
A plasma metabolomic signature of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy showing taurine and nicotinamide deficiencies
Abstract
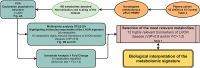
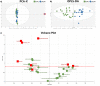
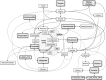
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is the most common disorder due to mitochondrial DNA mutations and complex I deficiency. It is characterized by an acute vision loss, generally in young adults, with a higher penetrance in males. How complex I dysfunction induces the peculiar LHON clinical presentation remains an unanswered question. To gain an insight into this question, we carried out a non-targeted metabolomic investigation using the plasma of 18 LHON patients, during the chronic phase of the disease, comparing them to 18 healthy controls. A total of 500 metabolites were screened of which 156 were accurately detected. A supervised Orthogonal Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA) highlighted a robust model for disease prediction with a Q2 (cum) of 55.5%, with a reliable performance during the permutation test (cross-validation analysis of variance, P-value = 5.02284e-05) and a good prediction of a test set (P = 0.05). This model highlighted 10 metabolites with variable importance in the projection (VIP) > 0.8. Univariate analyses revealed nine discriminating metabolites, six of which were the same as those found in the Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures Discriminant Analysis model. In total, the 13 discriminating metabolites identified underlining dietary metabolites (nicotinamide, taurine, choline, 1-methylhistidine and hippurate), mitochondrial energetic substrates (acetoacetate, glutamate and fumarate) and purine metabolism (inosine). The decreased concentration of taurine and nicotinamide (vitamin B3) suggest interesting therapeutic targets, given their neuroprotective roles that have already been demonstrated for retinal ganglion cells. Our results show a reliable predictive metabolomic signature in the plasma of LHON patients and highlighted taurine and nicotinamide deficiencies.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Mascialino, B., Leinonen, M. and Meier, T. (2011) Meta-analysis of the prevalence of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy mtDNA mutations in Europe. Eur. J. Ophthalmol., 22, 461–465. - PubMed
-
- Milea, D., Amati-Bonneau, P., Reynier, P. and Bonneau, D. (2010) Genetically determined optic neuropathies. Curr. Opin. Neurol., 23, 24–28. - PubMed
-
- Carelli, V., Carbonelli, M., deCoo, I.F., Kawasaki, A., Klopstock, T., Lagrèze, W.A., La Morgia, C., Newman, N.J., Orssaud, C., Pott, J.W.R.et al. (2017) International consensus statement on the clinical and therapeutic management of Leber hereditary optic neuropathy. J. Neuroophthalmol., 37, 371–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

