iPREFACE score: Integrated score index to predict fetal acidemia by intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring
- PMID: 33438340
- PMCID: PMC8048540
- DOI: 10.1111/jog.14652
iPREFACE score: Integrated score index to predict fetal acidemia by intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring
Abstract
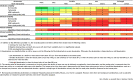
Aim: Cardiotocography is used worldwide to evaluate fetal well-being during pregnancy and labor. In past guidelines, the management plan was determined based on the assessment of the most severe waveform. There are no guidelines for evaluating the integrated recurrent decelerations; however, we believe their assessment to be essential for predicting the status of the fetus. The objective of this study was to propose an indicator for performing medical interventions during labor by creating a scoring system that reflects integrated recurrent decelerations.
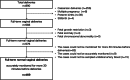
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we included data for only full-term single fetus births from vaginal deliveries. The score named the iPREFACE score (integrated score index to predict fetal acidemia by intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring) was calculated using cardiotocography findings from continuing 30 min before delivery. We examined the iPREFACE score and fetal acidemia association and calculated the cut-off iPREFACE scores for acidemia using receiver operating characteristic curves.
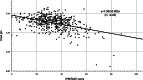
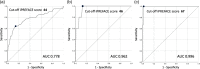
Results: The study included 469 delivery cases. Their iPREFACE scores exhibited a significant negative correlation with the umbilical artery blood pH (correlation coefficient; -0.43). The cut-off iPREFACE scores for the umbilical artery blood with pH <7.20, <7.10 and <7.0 were 44, 46 and 67, respectively (the areas under the curve were 0.776, 0.962 and 0.996, respectively).
Conclusion: The iPREFACE score may predict fetal acidemia and could be used as an indicator for timely medical interventions during labor. Because assessments using a cardiotocography are quick and easy to perform, the iPREFACE score could be a valuable tool in clinical practice.
Keywords: CTG; cardiotocography; electronic fetal monitoring; hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; umbilical artery blood pH.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The iPREFACE score is useful for predicting fetal acidemia: A retrospective cohort study of 113 patients who underwent emergency cesarean section for non-reassuring fetal status during labor.AJOG Glob Rep. 2024 Apr 4;4(2):100343. doi: 10.1016/j.xagr.2024.100343. eCollection 2024 May. AJOG Glob Rep. 2024. PMID: 38699222 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal duration of cardiotocography assessment using the iPREFACE score to predict fetal acidemia.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 29;12(1):13064. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17364-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35906383 Free PMC article.
-
Intrapartum electronic fetal heart rate monitoring to predict acidemia at birth with the use of deep learning.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2025 Jan;232(1):116.e1-116.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2024.04.022. Epub 2024 Apr 24. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2025. PMID: 38663662
-
Continuous cardiotocography during labour: Analysis, classification and management.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016 Jan;30:33-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2015.03.022. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016. PMID: 26165747 Review.
-
Relationship between the fetal biophysical profile score, umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry, and fetal blood acid-base status determined by cordocentesis.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Dec;169(6):1586-94. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90441-k. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993. PMID: 8267067 Review.
Cited by
-
The iPREFACE score is useful for predicting fetal acidemia: A retrospective cohort study of 113 patients who underwent emergency cesarean section for non-reassuring fetal status during labor.AJOG Glob Rep. 2024 Apr 4;4(2):100343. doi: 10.1016/j.xagr.2024.100343. eCollection 2024 May. AJOG Glob Rep. 2024. PMID: 38699222 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal duration of cardiotocography assessment using the iPREFACE score to predict fetal acidemia.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 29;12(1):13064. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17364-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35906383 Free PMC article.
-
Use of an artificial intelligence-based rule extraction approach to predict an emergency cesarean section.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2022 Jun;157(3):654-662. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.13888. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 34416018 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hon EH. The electronic evaluation of the fetal heart rate: Preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996;175:747–8. - PubMed
-
- Paul RH, Suidan AK, Yeh SY, Schifrin BS, Hon EH. Clinical fetal monitoring. VII. The evaluation and significance of intrapartum baseline FHR variability. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975;123:20–210. - PubMed
-
- Electronic fetal heart rate monitoring: Research guidelines for interpretation. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Research Planning Workshop. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;177:1385–90. - PubMed
-
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Clinical Effectiveness Support Unit . The Use of Electronic Fetal Monitoring: Evidence‐based Clinical Guideline No. 8. London: RCOG Press; 2001.
-
- Liston R, Sawchuck D, Young D. Society of Obstetrics and Gynaecologists of Canada; British Columbia Perinatal Health Program. Fetal Health Surveillance: Antepartum and Intrapartum Consensus Guideline. J Obstet Gynaecol Canada. 2007;29:S3–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

