PPARγ/NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad pathway are involved in the anti-fibrotic effects of levo-tetrahydropalmatine on liver fibrosis
- PMID: 33438347
- PMCID: PMC7875896
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16267
PPARγ/NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad pathway are involved in the anti-fibrotic effects of levo-tetrahydropalmatine on liver fibrosis
Abstract
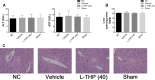
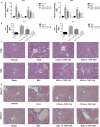
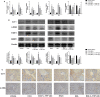
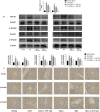
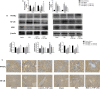
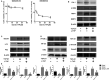
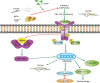
Liver fibrosis is a necessary stage in the development of chronic liver diseases to liver cirrhosis. This study aims to investigate the anti-fibrotic effects of levo-tetrahydropalmatine (L-THP) on hepatic fibrosis in mice and cell models and its underlying mechanisms. Two mouse hepatic fibrosis models were generated in male C57 mice by intraperitoneal injection of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) for 2 months and bile duct ligation (BDL) for 14 days. Levo-tetrahydropalmatine was administered orally at doses of 20 and 40 mg/kg. An activated LX2 cell model induced by TGF-β1 was also generated. The results showed that levo-tetrahydropalmatine alleviated liver fibrosis by inhibiting the formation of extracellular matrix (ECM) and regulating the balance between TIMP1 and MMP2 in the two mice liver fibrosis models and cell model. Levo-tetrahydropalmatine inhibited activation and autophagy of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) by modulating PPARγ/NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad pathway in vivo and in vitro. In conclusion, levo-tetrahydropalmatine attenuated liver fibrosis by inhibiting ECM deposition and HSCs autophagy via modulation of PPARγ/NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad pathway.
Keywords: PPARγ/NF-κB; TGF-β1/Smad; autophagy; levo-tetrahydropalmatine; liver fibrosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Liu T, Xu L, Wang C, et al. Alleviation of hepatic fibrosis and autophagy via inhibition of transforming growth factor‐beta1/Smads pathway through shikonin. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34(1):263–276. - PubMed
-
- Schuppan D, Ashfaq‐Khan M, Yang AT, Kim YO. Liver fibrosis: Direct antifibrotic agents and targeted therapies. Matrix Biol. 2018;68–69:435–451. - PubMed
-
- Campana L, Iredale JP. Regression of liver fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2017;37(1):1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81670472/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20YF1443300/the Yangfan Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission
- PTKWWS201801/the Health System Innovation Project of Shanghai Putuo Science and Technology Commission
- PTKWWS201903/the Health System Innovation Project of Shanghai Putuo Science and Technology Commission
- CFHPC2019031/WBN Hepatology Research Fund of China Hepatitis Prevention and Treatment Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

