Automated Adult Epilepsy Diagnostic Tool Based on Interictal Scalp Electroencephalogram Characteristics: A Six-Center Study
- PMID: 33438530
- PMCID: PMC9343226
- DOI: 10.1142/S0129065720500744
Automated Adult Epilepsy Diagnostic Tool Based on Interictal Scalp Electroencephalogram Characteristics: A Six-Center Study
Abstract
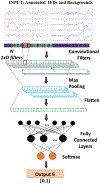
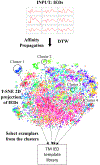
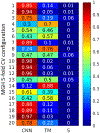
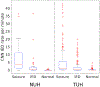
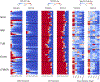
The diagnosis of epilepsy often relies on a reading of routine scalp electroencephalograms (EEGs). Since seizures are highly unlikely to be detected in a routine scalp EEG, the primary diagnosis depends heavily on the visual evaluation of Interictal Epileptiform Discharges (IEDs). This process is tedious, expert-centered, and delays the treatment plan. Consequently, the development of an automated, fast, and reliable epileptic EEG diagnostic system is essential. In this study, we propose a system to classify EEG as epileptic or normal based on multiple modalities extracted from the interictal EEG. The ensemble system consists of three components: a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based IED detector, a Template Matching (TM)-based IED detector, and a spectral feature-based classifier. We evaluate the system on datasets from six centers from the USA, Singapore, and India. The system yields a mean Leave-One-Institution-Out (LOIO) cross-validation (CV) area under curve (AUC) of 0.826 (balanced accuracy (BAC) of 76.1%) and Leave-One-Subject-Out (LOSO) CV AUC of 0.812 (BAC of 74.8%). The LOIO results are found to be similar to the interrater agreement (IRA) reported in the literature for epileptic EEG classification. Moreover, as the proposed system can process routine EEGs in a few seconds, it may aid the clinicians in diagnosing epilepsy efficiently.
Keywords: EEG classification; Epilepsy; convolutional neural networks; deep learning; interictal epileptiform discharges; multi-center study; spike detection.
Figures
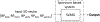
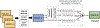
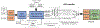
Similar articles
-
Improving automated diagnosis of epilepsy from EEGs beyond IEDs.J Neural Eng. 2022 Nov 24;19(6):10.1088/1741-2552/ac9c93. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac9c93. J Neural Eng. 2022. PMID: 36270485 Free PMC article.
-
Time-Frequency Decomposition of Scalp Electroencephalograms Improves Deep Learning-Based Epilepsy Diagnosis.Int J Neural Syst. 2021 Aug;31(8):2150032. doi: 10.1142/S0129065721500325. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Int J Neural Syst. 2021. PMID: 34278972 Free PMC article.
-
Automated Detection of Interictal Epileptiform Discharges from Scalp Electroencephalograms by Convolutional Neural Networks.Int J Neural Syst. 2020 Nov;30(11):2050030. doi: 10.1142/S0129065720500306. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Int J Neural Syst. 2020. PMID: 32812468 Free PMC article.
-
A review of signal processing and machine learning techniques for interictal epileptiform discharge detection.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Jan;168:107782. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107782. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38070202 Review.
-
Machine learning for detection of interictal epileptiform discharges.Clin Neurophysiol. 2021 Jul;132(7):1433-1443. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2021.02.403. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Clin Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 34023625 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a multimodal automatic interictal epileptiform discharge detection model: a prospective multi-center study.BMC Med. 2025 Aug 15;23(1):479. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-04316-3. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 40817241 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal avalanches in temporal lobe epilepsy as a noninvasive diagnostic tool investigating large scale brain dynamics.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 18;14(1):14039. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64870-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38890363 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic detection of epilepsy from EEGs using a temporal convolutional network with a self-attention layer.Biomed Eng Online. 2024 Jun 1;23(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12938-024-01244-w. Biomed Eng Online. 2024. PMID: 38824547 Free PMC article.
-
Improving automated diagnosis of epilepsy from EEGs beyond IEDs.J Neural Eng. 2022 Nov 24;19(6):10.1088/1741-2552/ac9c93. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac9c93. J Neural Eng. 2022. PMID: 36270485 Free PMC article.
-
An EEG dataset for interictal epileptiform discharge with spatial distribution information.Sci Data. 2025 Feb 7;12(1):229. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04572-1. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 39920162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thijs RD, Surges R, O’Brien TJ and Sander JW, Epilepsy in adults, Lancet 393 (2019) 689–701. - PubMed
-
- Adeli H, Zhou Z and Dadmehr N, Analysis of EEG records in an epileptic patient using wavelet transform, J. Neurosci. Methods 123(1) (2003) 69–87. - PubMed
-
- Frauscher B and Gotman J, Sleep, oscillations, interictal discharges, and seizures in human focal epilepsy, Neurobiol. Dis 127 (2019) 545–553. - PubMed
-
- Pillai J and Sperling MR, Interictal EEG and the diagnosis of epilepsy, Epilepsia 47 (2006) 14–22. - PubMed
-
- Fountain NB and Freeman JM, EEG is an essential clinical tool: Pro and con, Epilepsia 47 (2006) 23–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

