Implementation of Quality by Design (QbD) Principles in Regulatory Dossiers of Medicinal Products in the European Union (EU) Between 2014 and 2019
- PMID: 33439461
- PMCID: PMC8021511
- DOI: 10.1007/s43441-020-00254-9
Implementation of Quality by Design (QbD) Principles in Regulatory Dossiers of Medicinal Products in the European Union (EU) Between 2014 and 2019
Abstract
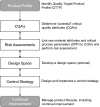
Background: Quality by Design (QbD) is a systematic risk-based approach to development, with predefined characteristics and quality risk management throughout the life cycle of a product. International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines Q8-Q11 give guidance on QbD applications with ICH Q8 (R2)-approved in 2009-describing the principles of QbD in detail. Since its adoption over 10 years ago, more information about QbD usage for the development of medicinal products is expected to be written in regulatory dossiers by companies.
Methods: The present study set out to evaluate the implementation of QbD principles and elements in all EU approved marketing applications (MA) (n = 494), based on information available in the European Public Assessment Reports (EPARs), for a period of six years (2014-2019), starting 5 years after QbD adoption.
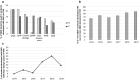
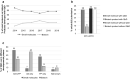
Results: Of the 494 MAs, 271 were submitted with a full dossier (article 8(3)). According to EMA (38%), out of the 271 full dossier submissions, only 104 were developed using full QbD. This figure did not increase during this period. Interestingly, between 2014 and 2019, several MAs were not developed via full QbD implementation but used one or more QbD elements during development, including design space. In addition, a higher percentage of small molecule products were developed with QbD as opposed to biotechnology-derived products (78% vs. 22%, respectively).
Conclusion: Overall, QbD during development of medicinal products is still not commonly described in dossiers. However, more companies started mentioning QbD elements, thus making it a promising step toward QbD as the standard for development in the future.
Keywords: Design space; Drug development; EMA; EPAR; QbD; Quality by Design.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Summary of the EMA Joint Regulators/Industry QbD workshop (London, UK; 28-29 January 2014).PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2016 Mar-Apr;70(2):163-76. doi: 10.5731/pdajpst.2015.006171. Epub 2016 Jan 21. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 26797977
-
Question-based review for pharmaceutical development: An enhanced quality approach.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2024 Feb;195:114174. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.114174. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2024. PMID: 38160986 Review.
-
Implementing quality by design for biotech products: Are regulators on track?MAbs. 2015;7(3):451-5. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1023058. MAbs. 2015. PMID: 25853461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality by design (QbD) approach in marketing authorization procedures of Non-Biological Complex Drugs: A critical evaluation.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2022 Sep;178:1-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2022.07.014. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2022. PMID: 35908664 Review.
-
Risk-based Process Development of Biosimilars as Part of the Quality by Design Paradigm.PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2013 Nov-Dec;67(6):569-80. doi: 10.5731/pdajpst.2013.00943. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 24265299
Cited by
-
Quality assessment strategy development and analytical method selection of GMP grade biological drugs for gene and cell therapy.BBA Adv. 2025 Feb 19;7:100151. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2025.100151. eCollection 2025. BBA Adv. 2025. PMID: 40094061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and Optimization of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Loaded with Triamcinolone Acetonide.Molecules. 2023 Jul 29;28(15):5747. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155747. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570717 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging the Gap: Quality by Design as a Catalyst for Enhanced Quality Management Systems in Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025;22(4):e15701638312326. doi: 10.2174/0115701638312326240918093333. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2025. PMID: 39350408 Review.
-
A narrative review on problems in product quality, regulatory system constraints, and the concept of quality by design as a solution for quality assurance of African medicines.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 3;11:1472495. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1472495. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39421861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle Therapeutics in Clinical Perspective: Classification, Marketed Products, and Regulatory Landscape.Small. 2025 Jul;21(29):e2502315. doi: 10.1002/smll.202502315. Epub 2025 Jun 2. Small. 2025. PMID: 40454890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nasr N. Risk Based CMC Review Paradigm. Advisory Committee for Pharmaceutical Science Meeting. 2004;2:20–21.
-
- ICH Q8 (R2). Pharmaceutical development, ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guidelines. International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. 2009.
-
- Tambe K, Bonde S. A review on: applications of pharmaceutical quality by design in product development. World J Pharm Sci. 2017;5:58–70.
-
- ICH Q9. Quality Risk Management. ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guidelines. International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. 2006.
-
- ICH Q10. Pharmaceutical Quality System, ICH Tripartite Guidelines. International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. 2007.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

