Disruption of circadian timing increases synaptic inhibition and reduces cholinergic responsiveness in the dentate gyrus
- PMID: 33439521
- PMCID: PMC8048473
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.23301
Disruption of circadian timing increases synaptic inhibition and reduces cholinergic responsiveness in the dentate gyrus
Abstract
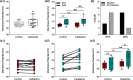
We investigated synaptic mechanisms in the hippocampus that could explain how loss of circadian timing leads to impairments in spatial and recognition memory. Experiments were performed in hippocampal slices from Siberian hamsters (Phodopus sungorus) because, unlike mice and rats, their circadian rhythms are easily eliminated without modifications to their genome and without surgical manipulations, thereby leaving neuronal circuits intact. Recordings of excitatory postsynaptic field potentials and population spikes in area CA1 and dentate gyrus granule cells revealed no effect of circadian arrhythmia on basic functions of synaptic circuitry, including long-term potentiation. However, dentate granule cells from circadian-arrhythmic animals maintained a more depolarized resting membrane potential than cells from circadian-intact animals; a significantly greater proportion of these cells depolarized in response to the cholinergic agonist carbachol (10 μM), and did so by increasing their membrane potential three-fold greater than cells from the control (entrained) group. Dentate granule cells from arrhythmic animals also exhibited higher levels of tonic inhibition, as measured by the frequency of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic potentials. Carbachol also decreased stimulus-evoked synaptic excitation in dentate granule cells from both intact and arrhythmic animals as expected, but reduced stimulus-evoked synaptic inhibition only in cells from control hamsters. These findings show that loss of circadian timing is accompanied by greater tonic inhibition, and increased synaptic inhibition in response to muscarinic receptor activation in dentate granule cells. Increased inhibition would likely attenuate excitation in dentate-CA3 microcircuits, which in turn might explain the spatial memory deficits previously observed in circadian-arrhythmic hamsters.
Keywords: Siberian hamster; acetylcholine; carbachol; dentate; hippocampus; sex differences.
© 2021 The Authors. Hippocampus published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Suppression of Circadian Timing and Its Impact on the Hippocampus.Front Neurosci. 2021 Apr 8;15:642376. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.642376. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33897354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential effects of a benzodiazepine on synaptic transmissions in rat hippocampal neurons in vitro.Brain Res. 1997 Oct 31;773(1-2):98-107. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(97)00920-7. Brain Res. 1997. PMID: 9409710
-
Synaptic connections from multiple subfields contribute to granule cell hyperexcitability in hippocampal slice cultures.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Dec;84(6):2918-32. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.84.6.2918. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 11110821
-
Vagus nerve stimulation induced long-lasting enhancement of synaptic transmission and decreased granule cell discharge in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of urethane-anesthetized rats.Brain Res. 2013 Jan 25;1492:63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.11.024. Epub 2012 Nov 23. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23183039
-
Synaptic Plasticity and Excitation-Inhibition Balance in the Dentate Gyrus: Insights from In Vivo Recordings in Neuroligin-1, Neuroligin-2, and Collybistin Knockouts.Neural Plast. 2018 Feb 18;2018:6015753. doi: 10.1155/2018/6015753. eCollection 2018. Neural Plast. 2018. PMID: 29670649 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Awareness of the Interplay Between the Gut Microbiota and Circadian Rhythms.Pol J Microbiol. 2023 Dec 16;72(4):355-363. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2023-046. eCollection 2023 Dec 1. Pol J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38095865 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian desynchronization disrupts physiological rhythms of prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons in mice.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 6;13(1):9181. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35898-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37280307 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian activities of the brain MNK-eIF4E signalling axis contribute to diurnal rhythms of some cognitive functions.Eur J Neurosci. 2022 Jul;56(1):3553-3569. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15678. Epub 2022 May 7. Eur J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35481869 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Circadian Timing and Its Impact on the Hippocampus.Front Neurosci. 2021 Apr 8;15:642376. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.642376. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33897354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired Morris water task retention following T21 light dark cycle exposure is not due to reduced hippocampal c-FOS expression.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Oct 12;16:1025388. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1025388. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36311860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bell, L. A. , Bell, K. A. , & McQuiston, A. R. (2013). Synaptic muscarinic response types in hippocampal CA1 interneurons depend on different levels of presynaptic activity and different muscarinic receptor subtypes. Neuropharmacology, 73, 160–173. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.026 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

