Duration of Adjuvant Doublet Chemotherapy (3 or 6 months) in Patients With High-Risk Stage II Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 33439695
- PMCID: PMC8078416
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.01330
Duration of Adjuvant Doublet Chemotherapy (3 or 6 months) in Patients With High-Risk Stage II Colorectal Cancer
Erratum in
-
Erratum.J Clin Oncol. 2021 May 20;39(15):1691. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.00954. J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34000204 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: As oxaliplatin results in cumulative neurotoxicity, reducing treatment duration without loss of efficacy would benefit patients and healthcare providers.
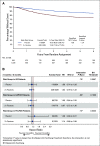
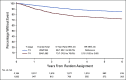
Patients and methods: Four of the six studies in the International Duration of Adjuvant Chemotherapy (IDEA) collaboration included patients with high-risk stage II colon and rectal cancers. Patients were treated (clinician and/or patient choice) with either fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) or capecitabine and oxaliplatin (CAPOX) and randomly assigned to receive 3- or 6-month treatment. The primary end point is disease-free survival (DFS), and noninferiority of 3-month treatment was defined as a hazard ratio (HR) of < 1.2- v 6-month arm. To detect this with 80% power at a one-sided type one error rate of 0.10, a total of 542 DFS events were required.
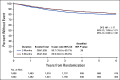
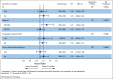
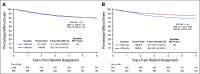
Results: 3,273 eligible patients were randomly assigned to either 3- or 6-month treatment with 62% receiving CAPOX and 38% FOLFOX. There were 553 DFS events. Five-year DFS was 80.7% and 83.9% for 3-month and 6-month treatment, respectively (HR, 1.17; 80% CI, 1.05 to 1.31; P [for noninferiority] .39). This crossed the noninferiority limit of 1.2. As in the IDEA stage III analysis, the duration effect appeared dependent on the chemotherapy regimen although a test of interaction was negative. HR for CAPOX was 1.02 (80% CI, 0.88 to 1.17), and HR for FOLFOX was 1.41 (80% CI, 1.18 to 1.68).
Conclusion: Although noninferiority has not been demonstrated in the overall population, the convenience, reduced toxicity, and cost of 3-month adjuvant CAPOX suggest it as a potential option for high-risk stage II colon cancer if oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy is suitable. The relative contribution of the factors used to define high-risk stage II disease needs better understanding.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00749450 NCT00646607 NCT01308086.
Figures
References
-
- Andre T Boni C Mounedji-Boudiaf L, et al. : Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2343-2351, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Kuebler JP Wieand HS O'Connell MJ, et al. : Oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: Results from NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol 25:2198-2204, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Schmoll HJ Tabernero J Maroun J, et al. : Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil/folinic acid as adjuvant therapy for stage III Colon cancer: Final results of the NO16968 randomized controlled phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 33:3733-3740, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Tournigand C Andre T Bonnetain F, et al. : Adjuvant therapy with fluorouracil and oxaliplatin in stage II and elderly patients (between ages 70 and 75 years) with colon cancer: Subgroup analyses of the Multicenter International Study of Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin in the Adjuvant Treatment of Colon Cancer trial. J Clin Oncol 30:3353-3360, 2012 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

