Tracking of COVID-19: A new real-time estimation using the Kalman filter
- PMID: 33439880
- PMCID: PMC7806155
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244474
Tracking of COVID-19: A new real-time estimation using the Kalman filter
Abstract
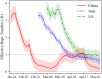
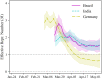
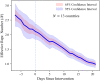
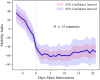
We develop a new method for estimating the effective reproduction number of an infectious disease () and apply it to track the dynamics of COVID-19. The method is based on the fact that in the SIR model, is linearly related to the growth rate of the number of infected individuals. This time-varying growth rate is estimated using the Kalman filter from data on new cases. The method is easy to implement in standard statistical software, and it performs well even when the number of infected individuals is imperfectly measured, or the infection does not follow the SIR model. Our estimates of for COVID-19 for 124 countries across the world are provided in an interactive online dashboard, and they are used to assess the effectiveness of non-pharmaceutical interventions in a sample of 14 European countries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Nishiura H, Chowell G. The Effective Reproduction Number as a Prelude to Statistical Estimation of Time-Dependent Epidemic Trends In: Chowell G, Hyman JM, Bettencourt LMA, Castillo-Chavez C, editors. Mathematical and Statistical Estimation Approaches in Epidemiology. Springer; 2009. p. 103–122.
-
- Dietz K. The estimation of the basic reproduction number for infectious diseases. Statistical Methods in Medical Research. 1993;2(1):23–41. - PubMed
-
- Chowell G, Brauer F. The Basic Reproduction Number of Infectious Diseases: Computation and Estimation Using Compartmental Epidemic Models In: Chowell G, Hyman JM, Bettencourt LMA, Castillo-Chavez C, editors. Mathematical and Statistical Estimation Approaches in Epidemiology. Springer; 2009. p. 1–30.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

