Inhibition of Nonfunctional Ras
- PMID: 33440168
- PMCID: PMC7897307
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.12.012
Inhibition of Nonfunctional Ras
Abstract
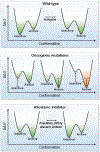
Intuitively, functional states should be targeted; not nonfunctional ones. So why could drugging the inactive K-Ras4BG12Cwork-but drugging the inactive kinase will likely not? The reason is the distinct oncogenic mechanisms. Kinase driver mutations work by stabilizing the active state and/or destabilizing the inactive state. Either way, oncogenic kinases are mostly in the active state. Ras driver mutations work by quelling its deactivation mechanisms, GTP hydrolysis, and nucleotide exchange. Covalent inhibitors that bind to the inactive GDP-bound K-Ras4BG12C conformation can thus work. By contrast, in kinases, allosteric inhibitors work by altering the active-site conformation to favor orthosteric drugs. From the translational standpoint this distinction is vital: it expedites effective pharmaceutical development and extends the drug classification based on the mechanism of action. Collectively, here we postulate that drug action relates to blocking the mechanism of activation, not to whether the protein is in the active or inactive state.
Keywords: K-Ras4B; KRAS; dimer; drug discovery; energy landscape; inhibitor; kinases.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Adams B, (2020). Eli Lilly crashes out of KRAS race as toxicity sees it ditch phase 1 effort. https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/eli-lilly-crashes-out-kras-race-as...
-
- Adjei AA (2001). Blocking oncogenic Ras signaling for cancer therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 93, 1062–1074. - PubMed
-
- Azam M, Latek RR, and Daley GQ (2003). Mechanisms of autoinhibition and STI-571/imatinib resistance revealed by mutagenesis of BCR-ABL. Cell 112, 831–843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

