Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-4035, Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM I-4034 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 Modulate Macrophage Gene Expression and Ameliorate Damage Markers in the Liver of Zucker-Lepr fa/fa Rats
- PMID: 33440736
- PMCID: PMC7826559
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13010202
Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-4035, Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM I-4034 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 Modulate Macrophage Gene Expression and Ameliorate Damage Markers in the Liver of Zucker-Lepr fa/fa Rats
Abstract
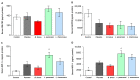
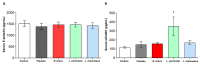
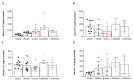
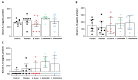
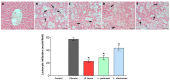
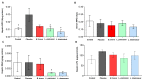
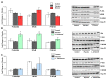
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has reached pandemic proportions worldwide. We have previously reported that the probiotic strains Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-4035, Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM I-4034 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 exert anti-inflammatory effects in the intestine of Zucker-Lepr fa/fa rats. In this work, we focused on their hepatic effects. M1 macrophages are related to inflammation and NAFLD pathogenesis, whereas M2 macrophages release anti-inflammatory mediators. We evaluated the effects of these 3 strains on macrophage polarization, inflammation and liver damage of Zucker-Lepr fa/fa rats. The animals received either a placebo or 1010 CFU of probiotics orally for 30 days. Nos2 and Cd86 mRNA levels were determined as markers of M1 macrophages, and Cd163 and Arg1 as M2 markers, respectively, by qRT-PCR. Liver damage was determined by lipid peroxidation, leukocyte infiltration and myeloperoxidase activity. We evaluated a panoply of circulating chemokines, the hepatic ratio P-Akt/Akt, NF-kB and P-NF-kB protein levels. All 3 probiotic strains modulated macrophage polarization in liver and circulating levels of inflammation-related mediators. L. paracasei CNCM I-4034 increased the ratio P-Akt/Akt and NF-kB protein levels. B. breve CNCM I-4035, L. paracasei CNCM I-4034 and L. rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 decreased both pro-inflammatory macrophage gene expression and leukocyte infiltration in the liver.
Keywords: NAFLD; inflammation; liver damage; macrophages; polarization; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fraternale A., Brundu S., Magnani M. Polarization and repolarization of macrophages. J. Clin. Cell Immunol. 2015;6:2.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

