A multi-stakeholder approach to the co-production of the research agenda for medicines optimisation
- PMID: 33441135
- PMCID: PMC7804576
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-021-06056-5
A multi-stakeholder approach to the co-production of the research agenda for medicines optimisation
Abstract
Background: Up to 50% of medicines are not used as intended, resulting in poor health and economic outcomes. Medicines optimisation is 'a person-centred approach to safe and effective medicines use, to ensure people obtain the best possible outcomes from their medicines'. The purpose of this exercise was to co-produce a prioritised research agenda for medicines optimisation using a multi-stakeholder (patient, researcher, public and health professionals) approach.
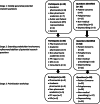
Methods: A three-stage, multiple method process was used including: generation of preliminary research questions (Stage 1) using a modified Nominal Group Technique; electronic consultation and ranking with a wider multi-stakeholder group (Stage 2); a face-to-face, one-day consensus meeting involving representatives from all stakeholder groups (Stage 3).
Results: In total, 92 research questions were identified during Stages 1 and 2 and ranked in order of priority during stage 3. Questions were categorised into four areas: 'Patient Concerns' [e.g. is there a shared decision (with patients) about using each medicine?], 'Polypharmacy' [e.g. how to design health services to cope with the challenge of multiple medicines use?], 'Non-Medical Prescribing' [e.g. how can the contribution of non-medical prescribers be optimised in primary care?], and 'Deprescribing' [e.g. what support is needed by prescribers to deprescribe?]. A significant number of the 92 questions were generated by Patient and Public Involvement representatives, which demonstrates the importance of including this stakeholder group when identifying research priorities.
Conclusions: A wide range of research questions was generated reflecting concerns which affect patients, practitioners, the health service, as well the ethical and philosophical aspects of the prescribing and deprescribing of medicines. These questions should be used to set future research agendas and funding commissions.
Keywords: Deprescribing; Medicines optimisation; Nominal group technique; Non-medical prescribing; Patient concerns; Polypharmacy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Bigdeli M, Peters D, Wagner A. Medicines in health systems: advancing access, affordability and appropriate use. 2014.
-
- Duerden M, Avery T, Payne R. Polypharmacy and medicines optimisation. Making it safe and sound. London: The King’s Fund; 2013.
-
- WHO . Medication without harm - global patient safety challenge on medication safety. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2017.
-
- Medicines optimisation: the safe and effective use of medicines to enable the best possible outcomes. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK305021/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK305021.pdf. Accessed 20 Sept 2019. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources