The spatial transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in China under the prevention and control measures at the early outbreak
- PMID: 33441168
- PMCID: PMC7804902
- DOI: 10.1186/s13690-021-00529-z
The spatial transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in China under the prevention and control measures at the early outbreak
Abstract
Background: Since severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was firstly reported in Wuhan City, China in December 2019, Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) that is caused by SARS-CoV-2 is predominantly spread from person-to-person on worldwide scales. Now, COVID-19 is a non-traditional and major public health issue the world is facing, and the outbreak is a global pandemic. The strict prevention and control measures have mitigated the spread of SARS-CoV-2 and shown positive changes with important progress in China. But prevention and control tasks remain arduous for the world. The objective of this study is to discuss the difference of spatial transmission characteristics of COVID-19 in China at the early outbreak stage with resolute efforts. Simultaneously, the COVID-19 trend of China at the early time was described from the statistical perspective using a mathematical model to evaluate the effectiveness of the prevention and control measures.
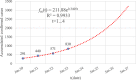
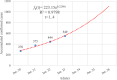
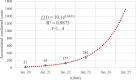
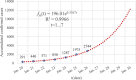
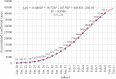
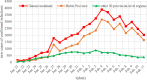
Methods: In this study, the accumulated number of confirmed cases publicly reported by the National Health Committee of the People's Republic of China (CNHC) from January 20 to February 11, 2020, were grouped into three partly overlapping regions: Chinese mainland including Hubei province, Hubei province alone, and the other 30 provincial-level regions on Chinese mainland excluding Hubei province, respectively. A generalized-growth model (GGM) was used to estimate the basic reproduction number to evaluate the transmissibility in different spatial locations. The prevention and control of COVID-19 in the early stage were analyzed based on the number of new cases of confirmed infections daily reported.
Results: Results indicated that the accumulated number of confirmed cases reported from January 20 to February 11, 2020, is well described by the GGM model with a larger correlation coefficient than 0.99. When the accumulated number of confirmed cases is well fitted by an exponential function, the basic reproduction number of COVID-19 of the 31 provincial-level regions on the Chinese mainland, Hubei province, and the other 30 provincial-level regions on the Chinese mainland excluding Hubei province, is 2.68, 6.46 and 2.18, respectively. The consecutive decline of the new confirmed cases indicated that the prevention and control measures taken by the Chinese government have contained the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in a short period.
Conclusions: The estimated basic reproduction number thorough GGM model can reflect the spatial difference of SARS-CoV-2 transmission in China at the early stage. The strict prevention and control measures of SARS-CoV-2 taken at the early outbreak can effectively reduce the new confirmed cases outside Hubei and have mitigated the spread and yielded positive results since February 2, 2020. The research results indicated that the outbreak of COVID-19 in China was sustaining localized at the early outbreak stage and has been gradually curbed by China's resolute efforts.
Keywords: Basic reproduction number; COVID-19; Early outbreak phase; Generalized-growth model; Prevention and control measures; Spatial transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gates B. Responding to Covid-19 — a once-in-a-century pandemic? N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1677–1679. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Weekly operational update on COVID-19. 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

