The immunological impact of adenovirus early genes on vaccine-induced responses in mice and nonhuman primates
- PMID: 33441339
- PMCID: PMC8092689
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02253-20
The immunological impact of adenovirus early genes on vaccine-induced responses in mice and nonhuman primates
Abstract
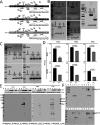
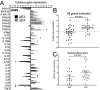
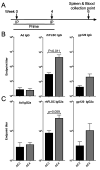
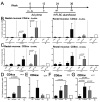
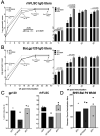
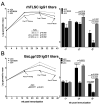
Adenovirus (Ad) is being explored for use in the prevention and treatment of a variety of infectious diseases and cancers. Ad with a deletion in early region 3 (ΔE3) provokes a stronger immune response than Ad with deletions in early regions 1 and E3 (ΔE1/ΔE3). The ΔE1/ΔE3 Ads are more popular because they can carry a larger transgene and because of the deleted E1 (E1A and E1B), are perceived safer for clinical use. Ad with a deletion in E1B55K (ΔE1B55K) has been in phase III clinical trials for use in cancer therapy in the US and has been approved for use in head and neck tumor therapy in China, demonstrating that Ad containing E1A are safe for clinical use. We have shown previously that ΔE1B55K Ad, even while promoting lower levels of an inserted transgene, promoted similar levels of transgene-specific immune responses as a ΔE3 Ad. Products of the Ad early region 4 (E4) limit the ability of cells to mount an innate immune response. Using this knowledge, we deleted the Ad E4 open reading frames 1-4 (E4orf1-4) from the ΔE1B55K Ad. Here, we show that innate cytokine network genes are elevated in the ΔE4 Ad-infected cells beyond that of ΔE3 Ad-infected cells. Further, in immunized mice the IgG2a subclass was favored as was the IgG1 subclass in immunized nonhuman primates. Thus, Ad E4 impacts immune responses in cells, in immunized mice, and immunized nonhuman primates. These Ad may offer advantages that are beneficial for clinical use.Importance: Adenovirus (Ad) is being explored for use in the prevention and treatment of a variety of infectious diseases and cancers. Here we provide evidence in cells, mice, and nonhuman primates supporting the notion that Ad early gene-products limit specific immune responses. Ad constructed with deletions in early genes and expressing HIV envelope protein was shown to induce greater HIV-specific cellular immune responses and higher titer antibodies compared to the parental Ad with the early genes. In addition to eliciting enhanced immunity, the deleted Ad possesses more space for insertion of additional or larger transgenes needed for targeting other infectious agents or cancers.
Copyright © 2021 Sangare et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
E4orf1 Suppresses E1B-Deleted Adenovirus Vaccine-Induced Immune Responses.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Feb 15;10(2):295. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020295. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214753 Free PMC article.
-
High-capacity adenoviral vectors circumvent the limitations of ΔE1 and ΔE1/ΔE3 adenovirus vectors to induce multispecific transgene product-directed CD8 T-cell responses.J Gene Med. 2011 Dec;13(12):648-57. doi: 10.1002/jgm.1629. J Gene Med. 2011. PMID: 22095925
-
Influence of E3 region on conditionally replicative adenovirus mediated cytotoxicity in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Jun;8(12):1125-32. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.12.8445. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19448394
-
Induction and inhibition of innate inflammatory responses by adenovirus early region proteins.Viral Immunol. 2005;18(1):79-88. doi: 10.1089/vim.2005.18.79. Viral Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15802954 Review.
-
Adenovirus vector induced innate immune responses: impact upon efficacy and toxicity in gene therapy and vaccine applications.Virus Res. 2008 Mar;132(1-2):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.10.005. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 18036698 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
E4orf1 Suppresses E1B-Deleted Adenovirus Vaccine-Induced Immune Responses.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Feb 15;10(2):295. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020295. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barouch DH, Liu J, Li H, Maxfield LF, Abbink P, Lynch DM, Iampietro MJ, SanMiguel A, Seaman MS, Ferrari G, Forthal DN, Ourmanov I, Hirsch VM, Carville A, Mansfield KG, Stablein D, Pau MG, Schuitemaker H, Sadoff JC, Billings EA, Rao M, Robb ML, Kim JH, Marovich MA, Goudsmit J, Michael NL. 2012. Vaccine protection against acquisition of neutralization-resistant SIV challenges in rhesus monkeys. Nature 482:89–93. doi:10.1038/nature10766. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abbink P, Maxfield LF, Ng’ang’a D, Borducchi EN, Iampietro MJ, Bricault CA, Teigler JE, Blackmore S, Parenteau L, Wagh K, Handley SA, Zhao G, Virgin HW, Korber B, Barouch DH. 2015. Construction and evaluation of novel rhesus monkey adenovirus vaccine vectors. J Virol 89:1512–1522. doi:10.1128/JVI.02950-14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gurwith M, Lock M, Taylor EM, Ishioka G, Alexander J, Mayall T, Ervin JE, Greenberg RN, Strout C, Treanor JJ, Webby R, Wright PF. 2013. Safety and immunogenicity of an oral, replicating adenovirus serotype 4 vector vaccine for H5N1 influenza: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 study. Lancet Infect Dis 13:238–250. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70345-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

