Oxysterols Modulate the Acute Effects of Ethanol on Hippocampal N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptors, Long-Term Potentiation, and Learning
- PMID: 33441369
- PMCID: PMC8051516
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.120.000376
Oxysterols Modulate the Acute Effects of Ethanol on Hippocampal N-Methyl-d-Aspartate Receptors, Long-Term Potentiation, and Learning
Abstract
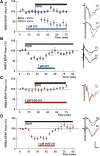
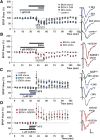
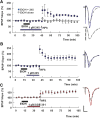
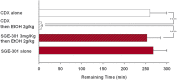
Ethanol is a noncompetitive inhibitor of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and acutely disrupts hippocampal synaptic plasticity and learning. In the present study, we examined the effects of oxysterol positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) of NMDARs on ethanol-mediated inhibition of NMDARs, block of long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) in rat hippocampal slices, and defects in one-trial learning in vivo. We found that 24S-hydroxycholesterol and a synthetic oxysterol analog, SGE-301, overcame effects of ethanol on NMDAR-mediated synaptic responses in the CA1 region but did not alter acute effects of ethanol on LTD; the synthetic oxysterol, however, overcame acute inhibition of LTP. In addition, both oxysterols overcame persistent effects of ethanol on LTP in vitro, and the synthetic analog reversed defects in one-trial inhibitory avoidance learning in vivo. These results indicate that effects of ethanol on both LTP and LTD arise by complex mechanisms beyond NMDAR antagonism and that oxysterol NMDAR PAMS may represent a novel approach for preventing and reversing acute ethanol-mediated changes in cognition. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Ethanol acutely inhibits hippocampal NMDARs, LTP, and learning. This study found that certain oxysterols that are NMDAR-positive allosteric modulators can overcome the acute effects of ethanol on NMDARs, LTP, and learning. Oxysterols differ in their effects from agents that inhibit integrated cellular stress responses.
Copyright © 2021 by The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C.F.Z is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Sage Therapeutics. J.J.D. is employed by Sage Therapeutics. Sage Therapeutics did not fund this research. Y.I. and S.J.M. have no conflicts of interest to disclose. There are no other competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Báez-Becerra C, Filipello F, Sandoval-Hernández A, Arboleda H, Arboleda G (2018) Liver X receptor agonist GW3965 regulates synaptic function upon amyloid beta exposure in hippocampal neurons. Neurotox Res 33:569–579. - PubMed
-
- Burlot M-A, Braudeau J, Michaelsen-Preusse K, Potier B, Ayciriex S, Varin J, Gautier B, Djelti F, Audrain M, Dauphinot L, et al. (2015) Cholesterol 24-hydroxylase defect is implicated in memory impairments associated with Alzheimer-like Tau pathology. Hum Mol Genet 24:5965–5976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

