OXA-181-Like Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae ST14, ST15, ST23, ST48, and ST231 from Septicemic Neonates: Coexistence with NDM-5, Resistome, Transmissibility, and Genome Diversity
- PMID: 33441403
- PMCID: PMC7845606
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.01156-20
OXA-181-Like Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae ST14, ST15, ST23, ST48, and ST231 from Septicemic Neonates: Coexistence with NDM-5, Resistome, Transmissibility, and Genome Diversity
Abstract
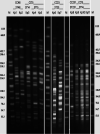
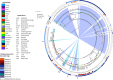
Studies on the epidemiology and genomes of isolates harboring OXA-48-like genes in septicemic neonates are rare. Here, isolates producing these carbapenemases which emerged and persisted in an Indian neonatal unit were characterized in terms of their resistome, transmissibility, and genome diversity. Antibiotic susceptibility and whole-genome sequencing were carried out. The sequence types, resistome, virulome, mobile genetic elements, and transmissibility of carbapenem-resistant plasmids were evaluated. Core genome analysis of isolates was shown in a global context with other OXA-48-like carbapenemase-harboring genomes, including those from neonatal studies. Eleven OXA-48-like carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (blaOXA-181, n = 7 and blaOXA-232, n = 4) isolates belonging to diverse sequence types (ST14, ST15, ST23, ST48, and ST231) were identified. blaOXA-181/OXA-232 and blaNDM-5 were found in a high-risk clone, ST14 (n = 4). blaOXA-181/OXA-232 were in small, nonconjugative ColKP3 plasmids located on truncated Tn2013, whereas blaNDM-5 was in self-transmissible, conjugative IncFII plasmids, within truncated Tn125 Conjugal transfer of blaOXA-181/OXA-232 was observed in the presence of blaNDM-5 The study strains were diverse among themselves and showed various levels of relatedness with non-neonatal strains from different parts of the world and similarity with neonatal strains from Tanzania and Ghana when compared with a representative collection of carbapenemase-positive K. pneumoniae strains. We found that blaOXA-181/OXA-232-harboring isolates from a single neonatal unit had remarkably diverse genomes, ruling out clonal spread and emphasizing the extent of plasmid spreading across different STs. This study is probably the first to report the coexistence of blaOXA-181/232 and blaNDM-5 in neonatal isolates.IMPORTANCE Neonatal sepsis is a leading cause of neonatal mortality in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Treatment of sepsis in this vulnerable population is dependent on antimicrobials, and resistance to these life-saving antimicrobials is worrisome. Carbapenemases, enzymes produced by bacteria, can make these antimicrobials useless. Our study describes how OXA-48-like carbapenemases in neonatal septicemic Klebsiella pneumoniae shows remarkable diversity in the genomes of the strains and relatedness with strains from other parts of world and also to some neonatal outbreak strains. It is also the first to describe such resistance due to coproduction of dual carbapenemases, (OXA)-48 and New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-5, in Klebsiella pneumoniae from neonatal settings. Carbapenemase genes situated on plasmids within high-risk international clones, as seen here, increase the ease and transfer of resistant genetic material. With the WHO treatment protocols not adequately poised to handle such infections, prompt attention to neonatal health care is required.
Keywords: ColKP3; India; NDM-5; OXA-181/232; WGS; core genome; dual carbapenemases; neonates; sepsis.
Copyright © 2021 Naha et al.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad N, Ali SM, Khan AU. 2019. Molecular characterization of novel sequence type of carbapenem-resistant New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in the neonatal intensive care unit of an Indian hospital. Int J Antimicrob Agents 53:525–529. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.12.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

