Relationship between basal sodium intake and the effects of dapagliflozin in albuminuric diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 33441623
- PMCID: PMC7806956
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79687-z
Relationship between basal sodium intake and the effects of dapagliflozin in albuminuric diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
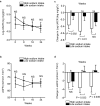
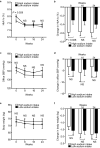
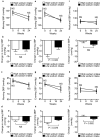
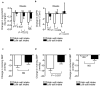
We investigated the impact of basal dietary sodium intake on the dapagliflozin-induced changes in albuminuria and blood pressure (BP) measured at home in patients with diabetic kidney disease (DKD).This was a secondary analysis of the Y-AIDA Study, in which DKD patients with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥ 45 ml/min/1.73 m2 and urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) ≥ 30 mg/g creatinine were administered dapagliflozin for 24 weeks, and dapagliflozin significantly improved albuminuria levels and home BP profiles. The effects on UACR, home-measured BP, and eGFR were compared between high- and low-sodium intake groups (HS and LS groups), which were created using baseline urinary sodium-to-creatinine ratio of 84 participants with available basal sodium-to-creatinine ratios. At baseline, clinic-/home-measured BPs, UACR, and eGFR, were comparable in the two groups. After 24 weeks, the reductions from baseline in ln-UACR were comparable in the two groups. In contrast, the reductions in evening home systolic BP and eGFR from baseline were larger in HS than in LS (BP: - 13 ± 2.08 vs. - 6 ± 1.88, P = 0.020; eGFR: - 3.33 ± 1.32 vs. 0.37 ± 1.29, P = 0.049). The home BP-lowering effects of dapagliflozin are larger in HS than LS, concomitant with a larger reduction in eGFR, suggesting a dapagliflozin-induced improvement in glomerular relative hyperfiltration in HS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improved home BP profile with dapagliflozin is associated with amelioration of albuminuria in Japanese patients with diabetic nephropathy: the Yokohama add-on inhibitory efficacy of dapagliflozin on albuminuria in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes study (Y-AIDA study).Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019 Aug 27;18(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0912-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 31455298 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of dapagliflozin on urinary albumin excretion in patients with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes: a prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021 Nov;9(11):755-766. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00243-6. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34619106 Clinical Trial.
-
Reduction in albuminuria with dapagliflozin cannot be predicted by baseline clinical characteristics or changes in most other risk markers.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019 Mar;21(3):720-725. doi: 10.1111/dom.13579. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019. PMID: 30414240 Free PMC article.
-
Albuminuria-lowering effect of dapagliflozin alone and in combination with saxagliptin and effect of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin on glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (DELIGHT): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019 Jun;7(6):429-441. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30086-5. Epub 2019 Apr 13. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30992195 Clinical Trial.
-
The kidney and type 2 diabetes mellitus: therapeutic implications of SGLT2 inhibitors.Postgrad Med. 2016;128(3):290-8. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2016.1147926. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Postgrad Med. 2016. PMID: 26821720 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutritional Strategies against Diabetic Nephropathy: Insights from Animal Studies and Human Trials.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 18;16(12):1918. doi: 10.3390/nu16121918. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38931271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor therapy: use in chronic kidney disease and adjunctive sodium restriction.Intern Med J. 2022 Oct;52(10):1666-1676. doi: 10.1111/imj.15727. Epub 2022 May 27. Intern Med J. 2022. PMID: 35257458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating the new pharmacological standard of care with traditional nutritional interventions in non-dialysis CKD.J Nephrol. 2025 Jan;38(1):61-73. doi: 10.1007/s40620-024-02135-y. Epub 2024 Nov 7. J Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39508986 Review.
-
Effect of a low-salt diet on chronic kidney disease outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2022 Jan 11;12(1):e050843. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-050843. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35017237 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous afferent arteriolopathy: a key concept for understanding blood pressure-dependent renal damage.Hypertens Res. 2024 Dec;47(12):3383-3396. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01916-z. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 39379463 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thomas, MC., Cooper, ME. & Zimmet, P. Changing epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and associated chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol.12, 73–81 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Allen, TJ. et al. Glomerular filtration rate in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Role of exchangeable sodium, vasoactive hormones, and insulin therapy. Diabetes.39, 1182–1190 (1990). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

