Baseline data report of the China Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS)
- PMID: 33441625
- PMCID: PMC7806992
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79531-4
Baseline data report of the China Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS)
Abstract
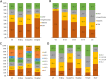
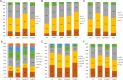
The number of patients on hemodialysis (HD) is rapidly increasing in China. As an Asian country with a large number of HD patients, understanding the status of Chinese HD patients has a special significance. We reported here the baseline data for China Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Pattern Study Phase 5 (DOPPS5). The DOPPS is an international prospective, observational cohort study. Patients were restricted to the initial sample of patients who participated in China DOPPS5. We summarized the baseline demographic and clinical data of patients. Results were weighted by facility sampling fraction. 1186 patients were initial patients in China DOPPS5. The mean age was 58.7 ± 3.5 years, with 54.6% males. The median dialysis vintage was 3.4 (1.5, 6.3) years. The main assigned primary end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) causes was chronic glomerulonephritis (45.9%), followed by diabetes (19.9%). 17.6% patients had hepatitis B infection, and 10.0% patients had hepatitis C infection. 25.9% patients had a single-pooled Kt/V < 1.2. 86.6% patients had albumin > 3.5 g/dl. 18.8% patients had hemoglobin < 9 g/dl. 66.5% patients had serum calcium in target range (8.4-10.2 mg/dl), 41.5% patients had serum phosphate in target range (3.5-5.5 mg/dl) and 51.2% patients maintained PTH in 150-600 pg/dl. 88.2% patients used fistula as their vascular access. Meanwhile, there were differences in the demographic, clinical, laboratory, and treatment characteristics among the three cities participated in China DOPPS. We observed a relatively higher albumin level and a higher rate of fistula usage in our patients. But it remains a major challenge to us on the management of CKD-MBD and anemia. This study did not include patients in small cities and remote areas, where the situation of HD patients might be worse than reported.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Young EW, et al. The Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS): An international hemodialysis study. Kidney Int. 2000;57:S74–S81. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.07413.x. - DOI
-
- Bieber B, et al. Two-times weekly hemodialysis in China: Frequency, associated patient and treatment characteristics and Quality of Life in the China Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns study. Nephrol. Dialysis Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dialysis Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Renal Assoc. 2014;29:1770–1777. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft472. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

