Assessment of the pulmonary adaptive immune response to Cladosporium cladosporioides infection using an experimental mouse model
- PMID: 33441700
- PMCID: PMC7806624
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79642-y
Assessment of the pulmonary adaptive immune response to Cladosporium cladosporioides infection using an experimental mouse model
Abstract
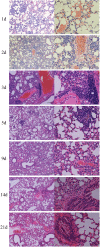
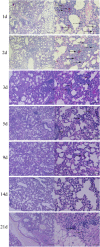
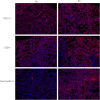
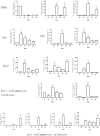
Cladosporium cladosporioides causes asthma and superficial and deep infections, mostly in immunodeficient individuals and animals. This study aimed to investigate whether C. cladosporioides spores can enter the lungs through pulmonary circulation and influence pulmonary immune response. We intravenously injected mice with C. cladosporioides spore suspension and conducted several assays on the lungs. Pulmonary hemorrhage symptoms and congestion were most severe on days 1, 2, and 3 post-inoculation (PI). Extensive inflammatory cell infiltration occurred throughout the period of infection. More spores and hyphae colonizing the lungs were detected on days 1, 2, and 3 PI, and fewer spores and hyphae were observed within 21 d of infection. Numerous macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils were observed on day 5 PI, along with upregulation of CD54, an intercellular adhesion molecule. Th1 and Th2 cells increased after infection; specifically, Th2 cells increased considerably on day 5 PI. These results suggest that days 2 and 5 PI represent the inflammatory peak in the lungs and that the Th2 and Th1 signaling pathways are potentially involved in pulmonary immune responses. In conclusion, the further adaptive immune responses played important roles in establishing effective pulmonary immunity against C. cladosporioides systemic infections based on innate immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Surface availability of beta-glucans is critical determinant of host immune response to Cladosporium cladosporioides.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Jul;132(1):159-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.01.003. Epub 2013 Feb 10. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23403046 Free PMC article.
-
Innate and mild Th17 cutaneous immune responses elicited by subcutaneous infection of immunocompetent mice with Cladosporium cladosporioides.Microb Pathog. 2022 Feb;163:105384. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105384. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 34974124
-
Dectin-1 and IL-17A suppress murine asthma induced by Aspergillus versicolor but not Cladosporium cladosporioides due to differences in β-glucan surface exposure.J Immunol. 2012 Oct 1;189(7):3609-17. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200589. Epub 2012 Sep 7. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22962686 Free PMC article.
-
[Airway immune responses in asthma].Arerugi. 2013 Dec;62(12):1565-74. Arerugi. 2013. PMID: 24608645 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Innate and adaptive type 2 immunity in lung allergic inflammation.Immunol Rev. 2017 Jul;278(1):162-172. doi: 10.1111/imr.12557. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28658559 Review.
Cited by
-
Meprin β expression modulates the interleukin-6 mediated JAK2-STAT3 signaling pathway in ischemia/reperfusion-induced kidney injury.Physiol Rep. 2022 Sep;10(18):e15468. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15468. Physiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36117389 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal Activity of Cell-Free Filtrate of Probiotic Bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC-7469 against Fungal Strains Isolated from a Historical Manuscript.Microorganisms. 2023 Apr 23;11(5):1104. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051104. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317078 Free PMC article.
-
Microsporum gypseum Isolated from Ailuropoda melanoleuca Provokes Inflammation and Triggers Th17 Adaptive Immunity Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 10;23(19):12037. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912037. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233337 Free PMC article.
-
Allicin as a Volatile or Nebulisable Antimycotic for the Treatment of Pulmonary Mycoses: In Vitro Studies Using a Lung Flow Test Rig.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 14;23(12):6607. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126607. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743050 Free PMC article.
-
Meprin β activity modulates cellular proliferation via trans-signaling IL-6-mediated AKT/ERK pathway in IR-induced kidney injury.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 30:rs.3.rs-5901359. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5901359/v1. Res Sq. 2025. PMID: 39975921 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Pourhassan N, Gagnon R, Wichard T, Bellenger JP. Identification of the Hydroxamate Siderophore Ferricrocin in Cladosporium cladosporioides. Nat. Product Commun. 2014;9:539–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

