Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-15 expression on peritumoral macrophages is a favorable prognostic factor for primary central nervous system lymphoma patients
- PMID: 33441719
- PMCID: PMC7806611
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79742-9
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-15 expression on peritumoral macrophages is a favorable prognostic factor for primary central nervous system lymphoma patients
Abstract
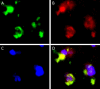
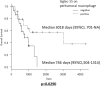
Sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-15 (Siglec-15) is a new immune checkpoint molecule and its role of primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) tumor microenvironment has been unclear. We explored the Siglec-15 and programed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in tumor tissues and analyzed the association between the expression of these molecules and overall survival in newly diagnosed PCNSL. A total of 60 patients diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in PCNSL were included in this study. The Siglec-15 and PD-L1 expression on tumor cells, intratumoral macrophages and peritumoral macrophages were immunohistochemically evaluated. The expression of Siglec-15 and PD-L1 was greater in macrophages than in tumor cells. Regarding peritumoral macrophages, the number of Siglec-15-positive samples (n = 24) was greater than the number of PD-L1-positive samples (n = 16). A multivariate Cox analysis showed that the Siglec-15 positivity of peritumoral macrophages and performance of high-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy were independent predictors of overall survival (hazard ratio: 0.295 and 0.322, respectively). The Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed that patients with Siglec-15-positive peritumoral macrophages had longer overall survival than those with Siglec-15-negative peritumoral macrophages (median overall survival: 3018 days and 746 days, respectively; p = 0.0290). Our findings indicate that the expression of Siglec-15 on peritumoral macrophages induces a favorable outcome in PCNSL patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Louis DN, et al. World Health Organization Histological Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2016.
-
- Morris PG, et al. Rituximab, methotrexate, procarbazine, and vincristine followed by consolidation reduced-dose whole-brain radiotherapy and cytarabine in newly diagnosed primary CNS lymphoma: final results and long-term outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013;31:3971–3979. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.50.4910. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

