Induction of spontaneous human neocentromere formation and long-term maturation
- PMID: 33443568
- PMCID: PMC7812830
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202007210
Induction of spontaneous human neocentromere formation and long-term maturation
Abstract
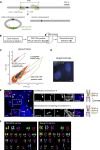
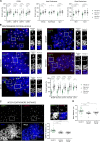
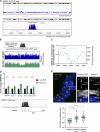
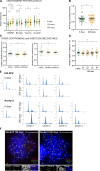
Human centromeres form primarily on α-satellite DNA but sporadically arise de novo at naive ectopic loci, creating neocentromeres. Centromere inheritance is driven primarily by chromatin containing the histone H3 variant CENP-A. Here, we report a chromosome engineering system for neocentromere formation in human cells and characterize the first experimentally induced human neocentromere at a naive locus. The spontaneously formed neocentromere spans a gene-poor 100-kb domain enriched in histone H3 lysine 9 trimethylated (H3K9me3). Long-read sequencing revealed this neocentromere was formed by purely epigenetic means and assembly of a functional kinetochore correlated with CENP-A seeding, eviction of H3K9me3 and local accumulation of mitotic cohesin and RNA polymerase II. At formation, the young neocentromere showed markedly reduced chromosomal passenger complex (CPC) occupancy and poor sister chromatin cohesion. However, long-term tracking revealed increased CPC assembly and low-level transcription providing evidence for centromere maturation over time.
© 2021 Murillo-Pineda et al.
Figures





Comment in
-
Truly epigenetic: A centromere finds a "neo" home.J Cell Biol. 2021 Mar 1;220(3):e202101027. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202101027. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33566070 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

