The role of SARS-CoV-2 target ACE2 in cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 33443816
- PMCID: PMC7875924
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16239
The role of SARS-CoV-2 target ACE2 in cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
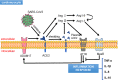
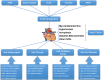
SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the global coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, attacks multiple organs of the human body by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) to enter cells. More than 20 million people have already been infected by the virus. ACE2 is not only a functional receptor of COVID-19 but also an important endogenous antagonist of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). A large number of studies have shown that ACE2 can reverse myocardial injury in various cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) as well as is exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic and anticardiomyocyte fibrosis effects by regulating transforming growth factor beta, mitogen-activated protein kinases, calcium ions in cells and other major pathways. The ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis plays a decisive role in the cardiovascular system to combat the negative effects of the ACE/angiotensin II/angiotensin II type 1 receptor axis. However, the underlying mechanism of ACE2 in cardiac protection remains unclear. Some approaches for enhancing ACE2 expression in CVDs have been suggested, which may provide targets for the development of novel clinical therapies. In this review, we aimed to identify and summarize the role of ACE2 in CVDs.
Keywords: ACE2; RAS; SARS-CoV-2; cardiovascular diseases.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

