New Deoxyisoaustamide Derivatives from the Coral-Derived Fungus Penicillium dimorphosporum KMM 4689
- PMID: 33445521
- PMCID: PMC7826743
- DOI: 10.3390/md19010032
New Deoxyisoaustamide Derivatives from the Coral-Derived Fungus Penicillium dimorphosporum KMM 4689
Abstract
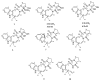
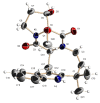
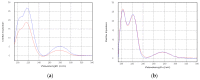
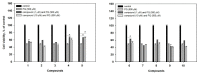
Seven new deoxyisoaustamide derivatives (1-7) together with known compounds (8-10) were isolated from the coral-derived fungus Penicillium dimorphosporum KMM 4689. Their structures were established using spectroscopic methods, X-ray diffraction analysis and by comparison with related known compounds. The absolute configurations of some alkaloids were determined based on CD and NOESY data as well as biogenetic considerations. The cytotoxic and neuroprotective activities of some of the isolated compounds were examined and structure-activity relationships were pointed out. New deoxyisoaustamides 4-6 at concentration of 1 µM revealed a statistical increase of PQ(paraquat)-treated Neuro-2a cell viability by 30-39%.
Keywords: Penicillium dimorphosporum; deoxyisoaustamide; neuroprotective activity; paraquat; prenylated indole diketopiperazines; secondary metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
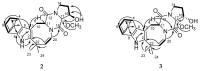
References
-
- Steyn P.S. The structures of five diketopiperazines from Aspergillus ustus. Tetrahedron. 1973;29:107–120. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)99384-6. - DOI
-
- Quang T.H., Lee D.-S., Sohn J.H., Kim Y.-C., Oh H. A new deoxyisoaustamide derivative from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. JF-72. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013;34:3109–3112. doi: 10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.10.3109. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

