IL-33 and Superantigenic Activation of Human Lung Mast Cells Induce the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors
- PMID: 33445787
- PMCID: PMC7828291
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10010145
IL-33 and Superantigenic Activation of Human Lung Mast Cells Induce the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors
Abstract
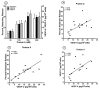
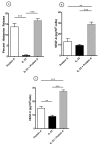
Human lung mast cells (HLMCs) express the high-affinity receptor FcεRI for IgE and are strategically located in different compartments of human lung, where they play a role in several inflammatory disorders and cancer. Immunoglobulin superantigens (e.g., protein A of Staphylococcus aureus and protein L of Peptostreptococcus magnus) bind to the variable regions of either the heavy (VH3) or light chain (κ) of IgE. IL-33 is a cytokine expressed by epithelial cells that exerts pleiotropic functions in the lung. The present study investigated whether immunoglobulin superantigens protein A and protein L and IL-33 caused the release of inflammatory (histamine), angiogenic (VEGF-A) and lymphangiogenic (VEGF-C) factors from HLMCs. The results show that protein A and protein L induced the rapid (30 min) release of preformed histamine from HLMCs. By contrast, IL-33 did not induce the release of histamine from lung mast cells. Prolonged incubation (12 h) of HLMCs with superantigens and IL-33 induced the release of VEGF-A and VEGF-C. Preincubation with IL-33 potentiated the superantigenic release of histamine, angiogenic and lymphangiogenic factors from HLMCs. Our results suggest that IL-33 might enhance the inflammatory, angiogenic and lymphangiogenic activities of lung mast cells in pulmonary disorders.
Keywords: IL-33; VEGF-A; VEGF-C; allergy; asthma; histamine; mast cell; protein A; protein L; superantigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Casolaro V., Galeone D., Giacummo A., Sanduzzi A., Melillo G., Marone G. Human Basophil/Mast Cell Releasability. V. Functional Comparisons of Cells Obtained from Peripheral Blood, Lung Parenchyma, and Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Asthmatics. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989;139:1375–1382. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.6.1375. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zilionis R., Engblom C., Pfirschke C., Savova V., Zemmour D., Saatcioglu H.D., Krishnan I., Maroni G., Meyerovitz C.V., Kerwin C.M., et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of Human and Mouse Lung Cancers Reveals Conserved Myeloid Populations across Individuals and Species. Immunity. 2019;50:1317–1334.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olivera A., Beaven M.A., Metcalfe D.D. Mast Cells Signal Their Importance in Health and Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018;142:381–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

