STOML2 potentiates metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting PINK1-mediated mitophagy and regulates sensitivity to lenvatinib
- PMID: 33446239
- PMCID: PMC7807703
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-01029-3
STOML2 potentiates metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting PINK1-mediated mitophagy and regulates sensitivity to lenvatinib
Abstract
Background: Dysregulation of both mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy is critical to sustain oncogenic signaling pathways. However, the mechanism of mitophagy in promoting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression remains poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the clinical significance and biological involvement of mitochondrial inner membrane protein STOML2 in HCC.
Methods: STOML2 was identified by gene expression profiles of HCC tissues and was measured in tissue microarray and cell lines. Gain/loss-of-function experiment was applied to study the biological function of STOML2 in HCC. Flow cytometry, Western blotting, laser confocal microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and co-immunoprecipitation were used to detect and analyze mitophagy. ChIP and luciferase reporter assay were conducted to evaluate the relationship between STOML2 and HIF-1α. The sensitivity to lenvatinib was assessed in HCC both in vitro and in vivo.
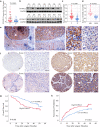
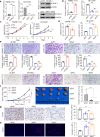
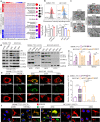
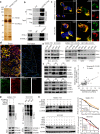
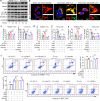
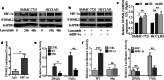
Results: Increased expression of STOML2 was found in HCC compared with paired peritumoral tissues. It was more significant in HCC with metastasis and correlated with worse overall survival and higher probability of recurrence after hepatectomy. Upregulation of STOML2 accelerated HCC cells colony formation, migration and invasion. Mechanically, TCGA dataset-based analysis showed enrichment of autophagy-related pathways in STOML2 highly-expressed HCC. Next, STOML2 was demonstrated to interact and stabilize PINK1 under cellular stress, amplify PINK1-Parkin-mediated mitophagy and then promote HCC growth and metastasis. Most interestingly, HIF-1α was upregulated and transcriptionally increased STOML2 expression in HCC cells under the treatment of lenvatinib. Furthermore, higher sensitivity to lenvatinib was found in HCC cells when STOML2 was downregulated. Combination therapy with lenvatinib and mitophagy inhibitor hydroxychloroquine obtained best efficacy.
Conclusions: Our findings suggested that STOML2 could amplify mitophagy through interacting and stabilizing PINK1, which promote HCC metastasis and modulate the response of HCC to lenvatinib. Combinations of pharmacologic inhibitors that concurrently block both angiogenesis and mitophagy may serve as an effective treatment for HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); Lenvatinib; Mitophagy; PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1); Stomatin-like protein 2 (STOML2).
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest with regard to the submitted manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

