Diffusion-weighted Imaging Allows for Downgrading MR BI-RADS 4 Lesions in Contrast-enhanced MRI of the Breast to Avoid Unnecessary Biopsy
- PMID: 33446565
- PMCID: PMC8406278
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3037
Diffusion-weighted Imaging Allows for Downgrading MR BI-RADS 4 Lesions in Contrast-enhanced MRI of the Breast to Avoid Unnecessary Biopsy
Abstract
Purpose: Diffusion-weighted imaging with the calculation of an apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) has been proposed as a quantitative biomarker on contrast-enhanced MRI (CE-MRI) of the breast. There is a need to approve a generalizable ADC cutoff. The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether a predefined ADC cutoff allows downgrading of BI-RADS 4 lesions on CE-MRI, avoiding unnecessary biopsies.
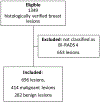
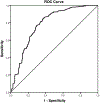
Experimental design: This was a retrospective, multicentric, cross-sectional study. Data from five centers were pooled on the individual lesion level. Eligible patients had a BI-RADS 4 rating on CE-MRI. For each center, two breast radiologists evaluated the images. Data on lesion morphology (mass, non-mass), size, and ADC were collected. Histology was the standard of reference. A previously suggested ADC cutoff (≥1.5 × 10-3 mm2/second) was applied. A negative likelihood ratio of 0.1 or lower was considered as a rule-out criterion for breast cancer. Diagnostic performance indices were calculated by ROC analysis.
Results: There were 657 female patients (mean age, 42; SD, 14.1) with 696 BI-RADS 4 lesions included. Disease prevalence was 59.5% (414/696). The area under the ROC curve was 0.784. Applying the investigated ADC cutoff, sensitivity was 96.6% (400/414). The potential reduction of unnecessary biopsies was 32.6% (92/282).
Conclusions: An ADC cutoff of ≥1.5 × 10-3 mm2/second allows downgrading of lesions classified as BI-RADS 4 on breast CE-MRI. One-third of unnecessary biopsies could thus be avoided.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Clauser P. received speaker’s fee from Siemens Healthcare GmBH.
The other authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bakker MF, de Lange SV, Pijnappel RM, et al.Supplemental MRI Screening for Women with Extremely Dense Breast Tissue. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(22):2091–2102. - PubMed
-
- Amitai Y, Scaranelo A, Menes TS, et al.Can breast MRI accurately exclude malignancy in mammographic architectural distortion? Eur Radiol. 2020;30(5):2751–2760. - PubMed
-
- Niell BL, Bhatt K, Dang P, Humphrey K. Utility of Breast MRI for Further Evaluation of Equivocal Findings on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018;211(5):1171–1178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

