ATDC binds to KEAP1 to drive NRF2-mediated tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 33446568
- PMCID: PMC7849366
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.344184.120
ATDC binds to KEAP1 to drive NRF2-mediated tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
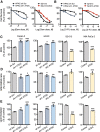
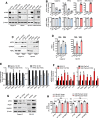
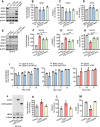
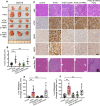
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is a lethal disease characterized by late diagnosis, propensity for early metastasis and resistance to chemotherapy. Little is known about the mechanisms that drive innate therapeutic resistance in pancreatic cancer. The ataxia-telangiectasia group D-associated gene (ATDC) is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and promotes tumor growth and metastasis. Our study reveals that increased ATDC levels protect cancer cells from reactive oxygen species (ROS) via stabilization of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2). Mechanistically, ATDC binds to Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1), the principal regulator of NRF2 degradation, and thereby prevents degradation of NRF2 resulting in activation of a NRF2-dependent transcriptional program, reduced intracellular ROS and enhanced chemoresistance. Our findings define a novel role of ATDC in regulating redox balance and chemotherapeutic resistance by modulating NRF2 activity.
Keywords: ATDC (Trim29); chemotherapeutic resistance; pancreatic cancer; tumor growth and invasion.
© 2021 Purohit et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Akino N, Wada-Hiraike O, Isono W, Terao H, Honjo H, Miyamoto Y, Tanikawa M, Sone K, Hirano M, Harada M, et al. 2019. Activation of Nrf2/Keap1 pathway by oral dimethylfumarate administration alleviates oxidative stress and age-associated infertility might be delayed in the mouse ovary. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 17: 23 10.1186/s12958-019-0466-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arora S, Bhardwaj A, Singh S, Srivastava SK, McClellan S, Nirodi CS, Piazza GA, Grizzle WE, Owen LB, Singh AP. 2013. An undesired effect of chemotherapy: gemcitabine promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness through reactive oxygen species-dependent, nuclear factor κB- and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α-mediated up-regulation of CXCR4. J Biol Chem 288: 21197–21207. 10.1074/jbc.M113.484576 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
