SIX2 and SIX3 coordinately regulate functional maturity and fate of human pancreatic β cells
- PMID: 33446570
- PMCID: PMC7849364
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.342378.120
SIX2 and SIX3 coordinately regulate functional maturity and fate of human pancreatic β cells
Abstract
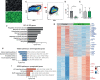
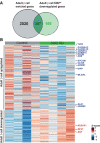
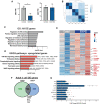
The physiological functions of many vital tissues and organs continue to mature after birth, but the genetic mechanisms governing this postnatal maturation remain an unsolved mystery. Human pancreatic β cells produce and secrete insulin in response to physiological cues like glucose, and these hallmark functions improve in the years after birth. This coincides with expression of the transcription factors SIX2 and SIX3, whose functions in native human β cells remain unknown. Here, we show that shRNA-mediated SIX2 or SIX3 suppression in human pancreatic adult islets impairs insulin secretion. However, transcriptome studies revealed that SIX2 and SIX3 regulate distinct targets. Loss of SIX2 markedly impaired expression of genes governing β-cell insulin processing and output, glucose sensing, and electrophysiology, while SIX3 loss led to inappropriate expression of genes normally expressed in fetal β cells, adult α cells, and other non-β cells. Chromatin accessibility studies identified genes directly regulated by SIX2. Moreover, β cells from diabetic humans with impaired insulin secretion also had reduced SIX2 transcript levels. Revealing how SIX2 and SIX3 govern functional maturation and maintain developmental fate in native human β cells should advance β-cell replacement and other therapeutic strategies for diabetes.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; islet; pancreas; transcription factor; β cells.
© 2021 Bevacqua et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK107507/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK108817/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK098085/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK128932/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007217/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001085/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK123743/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK116074/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK123716/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK126482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
