Lung ultrasound in early SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia and the LUS-CoV criteria
- PMID: 33446945
- PMCID: PMC7605644
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2020.1834658
Lung ultrasound in early SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia and the LUS-CoV criteria
Abstract
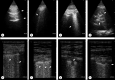
There is a scarcity of data on lung ultrasound (LUS) in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. As with many other pulmonary conditions, ultrasound may be a better diagnostic tool than routine chest radiography. In an era where computed tomography scanning is deferred because of the potential for cross-contamination, we evaluated the ability of LUS to detect a pattern of lung injury in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. A limited anterolateral LUS was performed to limit time spent in isolation rooms by ultrasound operators. We chose to use a hand-held ultrasound device due to portability and superior confidence in infection control. Both linear and phased array probes were used to obtain images of the pleura and lung. Of 69 patients who had lung ultrasound images saved and were included in the analysis, 36 were positive for SARS-CoV-2. Multifocal confluent B-lines, pleural irregularities, and the absence of moderate or large pleural effusions were the predominant pattern observed in most (86%) of SARS-CoV-2-positive patients. We evaluated the accuracy of the above criteria (LUS-CoV) and report a high sensitivity (91%) and specificity (86%) for SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. In conclusion, a characteristic sonographic pattern of multifocal confluent B-lines with irregular pleural markings was seen on LUS in patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; lung ultrasound.
Copyright © 2020 Baylor University Medical Center.
Figures
References
-
- American College of Radiology . ACR recommendations for the use of chest radiography and computed tomography (CT) for suspected COVID-19 infection. Updated March 22, 2020. https://www.acr.org/Advocacy-and-Economics/ACR-Position-Statements/Recom....
-
- Winkler MH, Touw HR, van de Ven PM, Twisk J, Tuinman PR.. Diagnostic accuracy of chest radiograph, and when concomitantly studied lung ultrasound, in critically ill patients with respiratory symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(7):e707–e714. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003129. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
