Kaleidoscopic fluorescent arrays for machine-learning-based point-of-care chemical sensing
- PMID: 33446959
- PMCID: PMC7802756
- DOI: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.129248
Kaleidoscopic fluorescent arrays for machine-learning-based point-of-care chemical sensing
Abstract
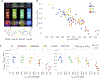
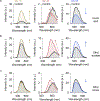
Multiplexed analysis allows simultaneous measurements of multiple targets, improving the detection sensitivity and accuracy. However, highly multiplexed analysis has been challenging for point-of-care (POC) sensing, which requires a simple, portable, robust, and affordable detection system. In this work, we developed paper-based POC sensing arrays consisting of kaleidoscopic fluorescent compounds. Using an indolizine structure as a fluorescent core skeleton, named Kaleidolizine (KIz), a library of 75 different fluorescent KIz derivatives were designed and synthesized. These KIz derivatives are simultaneously excited by a single ultraviolet (UV) light source and emit diverse fluorescence colors and intensities. For multiplexed POC sensing system, fluorescent compounds array on cellulose paper was prepared and the pattern of fluorescence changes of KIz on array were specific to target chemicals adsorbed on that paper. Furthermore, we developed a machine-learning algorithm for automated, rapid analysis of color and intensity changes of individual sensing arrays. We showed that the paper sensor arrays could differentiate 35 different volatile organic compounds using a smartphone-based handheld detection system. Powered by the custom-developed machine-learning algorithm, we achieved the detection accuracy of 97% in the VOC detection. The highly multiplexed paper sensor could have favorable applications for monitoring a broad-range of environmental toxins, heavy metals, explosives, pathogens.
Keywords: Fluorescent compound array; Indolizine; Pattern recognition; machine learning; multiplexing.
Figures



References
-
- Jalal AH, Alam F, Roychoudhury S, Umasankar Y, Pala N, Bhansali S. Prospects and Challenges of Volatile Organic Compound Sensors in Human Healthcare. ACS Sens. 3 (2018) 1246–1263. - PubMed
-
- Oh J-W, Chung W-J, Heo K, Jin H-E, Lee BY, Wang E, Zueger C, Wong W, Meyer J, Kim C, Lee S-Y, Kim W-G, Zemla M, Auer M, Hexemer A, Lee S-W. Biomimetic virus-based colourimetric sensors. Nat. Commun 5 (2014) 3043. - PubMed
-
- Shrivastava S, Trung TQ, Lee N-E. Recent progress, challenges, and prospects of fully integrated mobile and wearable point-of-care testing systems for self-testing. Chem. Soc. Rev 49 (2020) 1812–1866. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

