Engineered Nanomaterials: The Challenges and Opportunities for Nanomedicines
- PMID: 33447033
- PMCID: PMC7802788
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S288236
Engineered Nanomaterials: The Challenges and Opportunities for Nanomedicines
Abstract
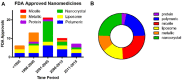
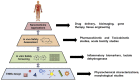
The emergence of nanotechnology as a key enabling technology over the past years has opened avenues for new and innovative applications in nanomedicine. From the business aspect, the nanomedicine market was estimated to worth USD 293.1 billion by 2022 with a perception of market growth to USD 350.8 billion in 2025. Despite these opportunities, the underlying challenges for the future of engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) in nanomedicine research became a significant obstacle in bringing ENMs into clinical stages. These challenges include the capability to design bias-free methods in evaluating ENMs' toxicity due to the lack of suitable detection and inconsistent characterization techniques. Therefore, in this literature review, the state-of-the-art of engineered nanomaterials in nanomedicine, their toxicology issues, the working framework in developing a toxicology benchmark and technical characterization techniques in determining the toxicity of ENMs from the reported literature are explored.
Keywords: Taylor dispersion analysis; asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation; engineered nanomaterials; nanomedicine; nanotoxicology; particle tracking analysis.
© 2021 Albalawi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Valavanidis A, Vlachogianni T. Engineered nanomaterials for pharmaceutical and biomedical products new trends, benefits and opportunities. Pharm Bioprocess. 2016;4:13.
-
- Analysis, M. Biomaterials and Medical Applications Nanotechnology 2020 Market Analysis. Vol. 3; 2020:2019–2020.
-
- Nikalje AP. Nanotechnology and its applications in medicine. Med Chem (Los Angeles). 2015;5. doi:10.4172/2161-0444.1000247 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

