Clinical Approach to Linear Hyperpigmentation: A Review Article
- PMID: 33447068
- PMCID: PMC7802900
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S280819
Clinical Approach to Linear Hyperpigmentation: A Review Article
Abstract
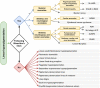
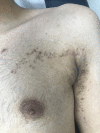
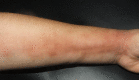
Linear hyperpigmentation is an unusual anatomical configuration in clinical dermatology. Owing to its rarity, consensus on the most effective method of classification is lacking. While linear hyperpigmentation generally follows Blaschko's lines, this is not universal. Clinical findings such as adherence to Blaschko's lines, associated morphological findings (including other cutaneous lesions), and systemic manifestations can be used to further characterize and diagnose variants of the disorder. Early detection of any underlying disease is vital, especially in cases with effective management, because the disorder may make it difficult to manage hyperpigmentation. Herein, we introduce a logical clinical diagnostic approach that represents a useful tool for dermatologists to efficiently evaluate patients presenting with linear hyperpigmentation. A simplified systematic and evidence-based approach is useful for this clinical condition owing to the heterogeneous causes and lack of specific diagnostic tools.
Keywords: Blaschko’s lines; approach; blaschkitis; hyperpigmentation; linear; pigmentary mosaicism.
© 2021 Alkhowailed et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures

References
-
- Bolognia JL, Orlow SJ, Glick SA. Lines of Blaschko. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31(2):157–190. - PubMed
-
- Happle R, Assim A. The lines of Blaschko on the head and neck. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44(4):612–615. - PubMed
-
- Lade NR, Saoji V, Singh AI. Blaschkoid lichen planus: not a koebner phenomenon. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19(4):17. - PubMed
-
- Sil A, Chakraborty S, Panigrahi A, Mondal S. Blaschkoid lichen planus occurring in childhood systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020;37(3):579–581. - PubMed
-
- Kanwar AJ, Dogra S, Handa S, Parsad D, Radotra BD. A study of 124 Indian patients with lichen planus pigmentosus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28(5):481–485. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

