The Impact of Different Induction Immunosuppressive Therapy on Long-Term Kidney Transplant Function When Measured by Iothalamate Clearance
- PMID: 33447312
- PMCID: PMC7781286
- DOI: 10.14740/jocmr4369
The Impact of Different Induction Immunosuppressive Therapy on Long-Term Kidney Transplant Function When Measured by Iothalamate Clearance
Abstract
Background: Improvement in short-term outcomes after kidney transplant has been achieved by using different induction and maintenance therapeutic approaches. Long-term outcomes have not matched the expectations of the transplant stakeholders. Our study aimed to address the early impact of induction agents on long-term outcome of kidney transplant when measured by iothalamate clearance.
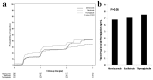
Methods: All adult kidney transplant recipients between January of 2012 and December of 2016 were reviewed. Six hundred forty-nine patients were divided into three groups based on the induction agent (basiliximab, alemtuzumab, and thymoglobulin). Protocoled 4 months and 48 months kidney allograft function evaluations with iothalamate clearance test were compared among the three groups.
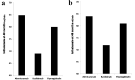
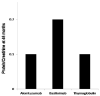
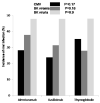
Results: Patients who received basiliximab were significantly older with no difference among African American and Caucasians. The 48 months assessment showed significant decline in median iothalamate clearance in basiliximab group at 49 mL/min vs. alemtuzumab group 64.8 mL/min and thymoglobulin 60 mL/min with P = 0.007. The basiliximab group developed a significant higher proteinuria measured by spot urine to creatinine ratio at 48 months.
Conclusions: The use of basiliximab as an induction agent for kidney transplant is associated with significant decline in kidney function 4 years post transplantation when measured by iothalamate clearance.
Keywords: Allografts; Induction; Iothalamate.
Copyright 2020, Jarmi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
