Complement Inhibition in Severe COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- PMID: 33447586
- PMCID: PMC7802050
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2020.616731
Complement Inhibition in Severe COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Abstract
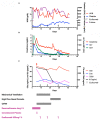
Most children with COVID-19 have asymptomatic or mild illness. Those who become critically ill suffer from acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and acute kidney injury (AKI). The rapid deterioration of lung function has been linked to microangiopathic and immune-mediated processes seen in the lungs of adult patients with COVID-19. The role of complement-mediated acute lung injury is supported by animal models of SARS-CoV, evaluation of lung tissue in those who died from COVID-19 and response of COVID-19 ARDS to complement inhibition. We present a summary of a child with COVID-19 disease treated with convalescent plasma and eculizumab and provide a detailed evaluation of the inflammatory pathways.
Keywords: COVID - 19; SARS-CoV-2; acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); children; complement; eculizumab; pediatric.
Copyright © 2020 Raghunandan, Josephson, Verkerke, Linam, Ingram, Zerra, Arthur, Stowell, Briones and Chonat.
Conflict of interest statement
CJ receives research funds from Terumo BCT, Octapharma and Medtronics. SC is a scientific advisor to Alexion, Novartis and Agios pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

