The STAPH Score: A Predictor of Staphylococcus aureus as the Causative Microorganism of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis
- PMID: 33447627
- PMCID: PMC7790121
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa504
The STAPH Score: A Predictor of Staphylococcus aureus as the Causative Microorganism of Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus (SA) is the most common causative microorganism in native vertebral osteomyelitis (NVO). Few studies have compared the clinical features of NVO due to SA (SA-NVO) and NVO due to other organisms (NSA-NVO). This study was conducted to validate a predictive score for SA-NVO to facilitate NVO treatment without broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents.
Methods: This retrospective study compared the clinical features of patients with SA-NVO and NSA-NVO who were diagnosed from 2004 to 2019. Univariate associations were assessed using χ 2, Fisher's exact, or Mann-Whitney U test. Multivariable analysis was conducted using logistic regression. The optimal age cutoff point was determined by classification and regression tree analysis.
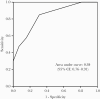
Results: Among 155 NVO patients, 98 (63.2%) had a microbiologically confirmed diagnosis: 40 (25.8%) with SA-NVO and 58 (37.4%) with NSA-NVO. Six predictors, either independently associated with SA-NVO or clinically relevant, were used to develop the STAPH prediction score: atopic dermatitis (Skin) (3 points); recent Trauma (2 points); Age < 67 years (1 point); Abscess (1 point); central venous Port catheter (2 points); and History of puncture (2 points). In a receiver operating characteristic analysis, the area under the curve was 0.84 (95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.91). The best cutoff point was 3. A score ≥3 had a sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of 58%, 84%, 84%, and 73%, respectively.
Conclusions: The STAPH score has relatively high specificity for use by clinicians to predict SA as the causative microorganism in patients with NVO until results of a confirmatory culture are available.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; clinical prediction rule; native vertebral osteomyelitis.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of pyogenic postoperative and native vertebral osteomyelitis.Spine J. 2019 May;19(5):880-887. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.11.012. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Spine J. 2019. PMID: 30500465
-
The utility of disc space and vertebral body specimens cell count differential for the diagnosis of native vertebral osteomyelitis: a prospective cohort study.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024 Dec;43(12):2371-2381. doi: 10.1007/s10096-024-04951-3. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39356370
-
Clinical features and outcome of vertebral osteomyelitis after spinal injection: is it worth the price?Infection. 2023 Jun;51(3):599-607. doi: 10.1007/s15010-023-02024-9. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Infection. 2023. PMID: 37071309 Free PMC article.
-
Rifampin Based Therapy for Patients With Staphylococcus aureus Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 25;78(1):40-47. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad560. Clin Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 37721158 Free PMC article.
-
Culture-Negative Native Vertebral Osteomyelitis: A Narrative Review of an Underdescribed Condition.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 28;13(19):5802. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195802. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39407862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gouliouris T, Aliyu S, Brown N. Spondylodiscitis: update on diagnosis and management. J Antimicrob Chemother 2010; 65:iii11–24. - PubMed
-
- Jensen AG, Espersen F, Skinhøj P, et al. Increasing frequency of vertebral osteomyelitis following Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in Denmark 1980–1990. J Infect 1997; 34:113–8. - PubMed
-
- Berbari EF, Kanj SS, Kowalski TJ, et al. 2015 Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of native vertebral osteomyelitis in adults. Clin Infect Dis 2015; 61:e26–46. - PubMed
-
- Ozuna RM, Delamarter RB. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis and postsurgical disc space infections. Orthop Clin North Am 1996; 27:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Mylona E, Samarkos M, Kakalou E, et al. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: a systematic review of clinical characteristics. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2009; 39:10–7. - PubMed