Blood pressure control in older adults with hypertension: A systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression
- PMID: 33447766
- PMCID: PMC7803055
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijchy.2020.100040
Blood pressure control in older adults with hypertension: A systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression
Abstract
Background: Managing blood pressure reduces CVD risk, but optimal treatment thresholds remain unclear as it is a balancing act to avoid hypotension-related adverse events.
Objectives: This systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression evaluated the benefits of intensive BP treatment in hypertensive older adults.
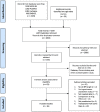
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library of Controlled Trials until January 31, 2020. Studies comparing different BP treatments/targets and/or active BP against placebo treatment, with a minimum 12 months follow-up, were included. Risk ratios (RR) and 95% CIs were calculated using a random effects model. The primary outcome was RR of major cardiovascular events (MCEs); secondary outcomes included myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, heart failure (HF), cardiovascular (CV) mortality, and all-cause mortality.
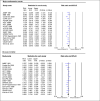
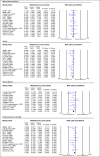
Results: We included 16 studies totaling 65,890 hypertensive participants (average age 69.4 years) with a follow-up period from 1.8 to 4.9 years. Intensive BP treatment significantly reduced the relative risk of MCEs by 26% (RR:0.74, 95%CI 0.64-0.86, p = 0.000; I 2 = 79.71%). RR of MI significantly reduced by 13% (RR:0.87, 95%CI 0.76-1.00, p = 0.052; I 2 = 0.00%), stroke by 28% (RR:0.72, 95%CI 0.64-0.82, p = 0.000; I 2 = 32.45%), HF by 47% (RR:0.53, 95% CI 0.43-0.66, p = 0.000; I 2 = 1.23%), and CV mortality by 24% (RR:0.76, 95%CI 0.66-0.89, p = 0.000; I 2 = 39.74%). All-cause mortality reduced by 17% (RR:0.83, 95%CI 0.73-0.93, p = 0.001; I 2 = 53.09%). Of the participants - 61% reached BP targets and 5% withdrew; with 1 hypotension-related event per 780 people treated.
Conclusions: Lower BP treatment targets are optimal for CV protection, effective, well-tolerated and safe, and support the latest hypertension guidelines.
Keywords: BP, blood pressure; Blood pressure treatment targets; CI, confidence interval; CV, cardiovascular; CVD, cardiovascular disease; Cardiovascular events; HF, heart failure; Hypertension; MCE, major cardiovascular event; Mortality; RR, relative risk or risk ratio.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors declare any conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of intensive blood pressure lowering on mortality and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 12;14(4):e0215362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215362. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30978254 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Blood Pressure Lowering With Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease Across Blood Pressure Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Intern Med. 2018 Jan 1;178(1):28-36. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.6015. JAMA Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29131895 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-blockers for suspected or diagnosed acute myocardial infarction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 17;12(12):CD012484. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012484.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31845756 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Intensive Blood Pressure Lowering in Older Hypertensive Patients.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Feb 7;69(5):486-493. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.077. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28153104 Review.
-
Effects of glucose-lowering and multifactorial interventions on cardiovascular and mortality outcomes: a meta-analysis of randomized control trials.Diabet Med. 2016 Mar;33(3):280-9. doi: 10.1111/dme.12885. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Diabet Med. 2016. PMID: 26282461 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of remote ischaemic conditioning on blood pressure response: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Cardiol Hypertens. 2021 Feb 23;8:100081. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchy.2021.100081. eCollection 2021 Mar. Int J Cardiol Hypertens. 2021. PMID: 33748739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Life's Essential 8: Optimizing Health in Older Adults.JACC Adv. 2023 Sep;2(7):100560. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2023.100560. Epub 2023 Aug 23. JACC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37664644 Free PMC article.
-
Time to Clinical Benefit of Intensive Blood Pressure Lowering in Patients 60 Years and Older With Hypertension: A Secondary Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.JAMA Intern Med. 2022 Jun 1;182(6):660-667. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2022.1657. JAMA Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35532917 Free PMC article.
-
Current Management of Hypertension in Older Adults.Drugs Aging. 2023 May;40(5):407-416. doi: 10.1007/s40266-023-01013-9. Epub 2023 Mar 18. Drugs Aging. 2023. PMID: 36933178 Review.
-
Safety, efficacy and delivery of isometric resistance training as an adjunct therapy for blood pressure control: a modified Delphi study.Hypertens Res. 2022 Mar;45(3):483-495. doi: 10.1038/s41440-021-00839-3. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Hypertens Res. 2022. PMID: 35017680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nguyen B., Bauman A., Ding D. Association between lifestyle risk factors and incident hypertension among middle-aged and older Australians. Prev. Med. 2019;118:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Harrap S.B., Lung T., Chalmers J. New blood pressure guidelines pose difficult choices for Australian physicians. Circ. Res. 2019;124(7):975–977. - PubMed
-
- Beckett N.S., Peters R., Fletcher A.E. Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;358(18):1887–1898. - PubMed
-
- Hansson L., Zanchetti A., Carruthers S.G. Effects of intensive blood-pressure lowering and low-dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. Lancet. 1998;351(9118):1755–1762. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

