Hypothesis: Unrecognized actions of ENaC blockade in improving refractory-resistant hypertension and residual cardiovascular risk
- PMID: 33447773
- PMCID: PMC7803029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijchy.2020.100048
Hypothesis: Unrecognized actions of ENaC blockade in improving refractory-resistant hypertension and residual cardiovascular risk
Keywords: Amiloride; Angiotensin II; ENaC; Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; Immunity in hypertension; Resistant hypertension; Sodium.
Figures
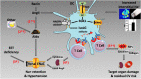
References
-
- Virani S., Alonso A., Benjamin E.J., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139–e596. https://doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Acelajado M.C., Pisoni R., Dudenbostel T., Dell'Italia L.J., Cartmill F., Bin Zhang B. Refractory hypertension: definition, prevalence and patient characteristics. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2012;14:7–12. https://doi:10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00556.x (Greenwich) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blacher J., Evans A., Arveiler D., Amouyel P., Ferrières J., Bingham A. On behalf of the PRIME Study Group, Residual coronary risk in men aged 50-59 years treated for hypertension and hyperlipidaemia in the population: the PRIME study. J. Hypertens. 2004;22:415–423. https://doi:10.1097/00004872-200402000-00028 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sim J.J., Bhandari S.K., Shi J., Liu I.L.A., Calhoun D.A., McGlynn E.A. Characteristics of resistant hypertension in a large, ethnically diverse hypertension population of an integrated health system. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013;88:1099–1107. https://doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.06.017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grigoryan L., Pavlik V.N., Hyman D.J. Characteristics, drug combinations and dosages of primary care patients with uncontrolled ambulatory blood pressure and high medication adherence. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2013;7:471–476. https://doi:10.1016/j.jash.2013.06.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

