Neutralizing activity to SARS-CoV-2 of convalescent and control plasma used in a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 33448402
- PMCID: PMC8014203
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.16283
Neutralizing activity to SARS-CoV-2 of convalescent and control plasma used in a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: There are limited data on the neutralizing activity of convalescent plasma (CP) administered in randomized controlled trials (RCT) of COVID-19 infection.
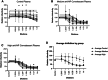
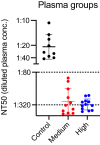
Study design and methods: As part of an RCT, CP was collected per FDA guidelines from individuals recovered from COVID-19 infection. CP donors had to have ≥145 optical density (OD) units (ideal target ≥300) using a semiquantitative, immunochromatographic test for IgG antibody to the nucleocapsid protein (NP) of SARS-CoV-2 (typical range 0-500 OD units). A random subset of samples [14 control plasma, 12 CP "medium-anti-NP" (145-299 OD units), and 13 CP "high" anti-NP (≥300 OD units)] were tested for neutralizing antibodies using an established viral luciferase antibody inhibition assay to detect the infection of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus that encoded spike protein (SARS2-Strunc ) on a human immunodeficiency virus 1 vector (NL43dEnvNanoLuc), using ACE2-expressing 293 T cells. The titer needed to neutralize 50% of viral activity (NT50) was calculated.
Results: The uptake of SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus by 293TACE2 cells was inhibited by pretreatment with CP compared to control CP (p < .001) with control plasma having a median (IQR) 50% neutralization titer (NT50) of 1:28 (1:16,1:36) compared to 1:334 (1:130,1:1295) and 1:324 (1:244,1:578), for medium anti-NP and high anti-NP CP units, respectively. The neutralizing activity of CP met minimum FDA criteria with neutralizing antibody titers >1:80 in 100% of randomly selected samples, using a conservative approach that excluded non-specific binding.
Discussion: Plasma from donors screened using an immunochromatographic test for IgG antibody to SARS-CoV-2 NP exhibited neutralizing activity meeting FDA's minimum standard in all randomly selected COVID-19 CP units.
Keywords: FFP transfusion; immunology (other than RBC serology).
© 2021 AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors disclosed any conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mair‐Jenkins J, Saavedra‐Campos M, Baillie JK, Cleary P, Khaw FM, Lim WS, et al. The effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral etiology: A systematic review and exploratory meta‐analysis. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:80–90. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

