The orchestrated cellular and molecular responses of the kidney to endotoxin define a precise sepsis timeline
- PMID: 33448928
- PMCID: PMC7810465
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.62270
The orchestrated cellular and molecular responses of the kidney to endotoxin define a precise sepsis timeline
Abstract
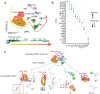
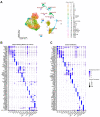
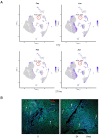
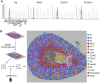
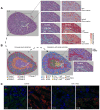
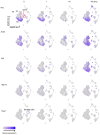
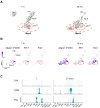
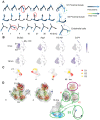
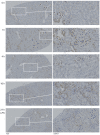
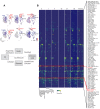
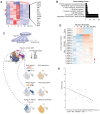
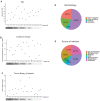
Sepsis is a dynamic state that progresses at variable rates and has life-threatening consequences. Staging patients along the sepsis timeline requires a thorough knowledge of the evolution of cellular and molecular events at the tissue level. Here, we investigated the kidney, an organ central to the pathophysiology of sepsis. Single-cell RNA-sequencing in a murine endotoxemia model revealed the involvement of various cell populations to be temporally organized and highly orchestrated. Endothelial and stromal cells were the first responders. At later time points, epithelial cells upregulated immune-related pathways while concomitantly downregulating physiological functions such as solute homeostasis. Sixteen hours after endotoxin, there was global cell-cell communication failure and organ shutdown. Despite this apparent organ paralysis, upstream regulatory analysis showed significant activity in pathways involved in healing and recovery. This rigorous spatial and temporal definition of murine endotoxemia will uncover precise biomarkers and targets that can help stage and treat human sepsis.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; human; immunology; inflammation; medicine; mouse; sepsis; single-cell RNA-seq.
© 2021, Janosevic et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DJ, JM, TM, AZ, FS, XX, HG, YL, KC, YC, SW, TE, BM, RM, ME, TH, PD No competing interests declared
Figures



Comment in
-
Sepsis gene signatures over time and space.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Apr;17(4):221. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00401-x. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33531662 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aibar S, González-Blas CB, Moerman T, Huynh-Thu VA, Imrichova H, Hulselmans G, Rambow F, Marine JC, Geurts P, Aerts J, van den Oord J, Atak ZK, Wouters J, Aerts S. SCENIC: single-cell regulatory network inference and clustering. Nature Methods. 2017;14:1083–1086. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4463. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aran D, Looney AP, Liu L, Wu E, Fong V, Hsu A, Chak S, Naikawadi RP, Wolters PJ, Abate AR, Butte AJ, Bhattacharya M. Reference-based analysis of lung single-cell sequencing reveals a transitional profibrotic macrophage. Nature Immunology. 2019;20:163–172. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0276-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao J, Cusanovich DA, Ramani V, Aghamirzaie D, Pliner HA, Hill AJ, Daza RM, McFaline-Figueroa JL, Packer JS, Christiansen L, Steemers FJ, Adey AC, Trapnell C, Shendure J. Joint profiling of chromatin accessibility and gene expression in thousands of single cells. Science. 2018;361:1380–1385. doi: 10.1126/science.aau0730. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- K08 DK107864/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI148282/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK097512/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL091816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079337/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK113223/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK080063/NIH Office of the Director
- UL1 TR002529/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK120524/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002901/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- P30 DK079312/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK107623/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK111651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003935/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

