The Hippo pathway: Horizons for innovative treatments of peripheral nerve diseases
- PMID: 33449435
- PMCID: PMC8455061
- DOI: 10.1111/jns.12431
The Hippo pathway: Horizons for innovative treatments of peripheral nerve diseases
Abstract
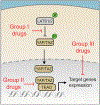
Initially identified in Drosophila, the Hippo signaling pathway regulates how cells respond to their environment by controlling proliferation, migration and differentiation. Many recent studies have focused on characterizing Hippo pathway function and regulation in mammalian cells. Here, we present a brief overview of the major components of the Hippo pathway, as well as their regulation and function. We comprehensively review the studies that have contributed to our understanding of the Hippo pathway in the function of the peripheral nervous system and in peripheral nerve diseases. Finally, we discuss innovative approaches that aim to modulate Hippo pathway components in diseases of the peripheral nervous system.
Keywords: Hippo; YAP/TAZ; nerve injury and regeneration; neurofibromatosis; peripheral neuropathy; schwann cell.
© 2021 Peripheral Nerve Society.
Figures


References
-
- Harvey KF, Pfleger CM, Hariharan IK. The Drosophila Mst ortholog, hippo, restricts growth and cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell. 2003;114:457–467. - PubMed
-
- Pantalacci S, Tapon N, Leopold P. The Salvador partner hippo promotes apoptosis and cell-cycle exit in Drosophila. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:921–927. - PubMed
-
- Udan RS, Kango-Singh M, Nolo R, Tao C, Halder G. Hippo promotes proliferation arrest and apoptosis in the Salvador/warts pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:914–920. - PubMed
-
- Wu S, Huang J, Dong J, Pan D. Hippo encodes a Ste-20 family protein kinase that restricts cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in conjunction with Salvador and warts. Cell. 2003;114:445–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

