Pannexin 1 channels control the hemodynamic response to hypoxia by regulating O2-sensitive extracellular ATP in blood
- PMID: 33449849
- PMCID: PMC7988759
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00651.2020
Pannexin 1 channels control the hemodynamic response to hypoxia by regulating O2-sensitive extracellular ATP in blood
Abstract
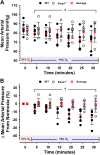
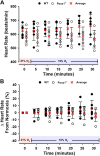
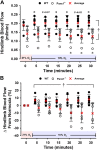
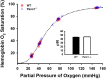
Pannexin 1 (Panx1) channels export ATP and may contribute to increased concentration of the vasodilator ATP in plasma during hypoxia in vivo. We hypothesized that Panx1 channels and associated ATP export contribute to hypoxic vasodilation, a mechanism that facilitates the matching of oxygen delivery to metabolic demand of tissue. Male and female mice devoid of Panx1 (Panx1-/-) and wild-type controls (WT) were anesthetized, mechanically ventilated, and instrumented with a carotid artery catheter or femoral artery flow transducer for hemodynamic and plasma ATP monitoring during inhalation of 21% (normoxia) or 10% oxygen (hypoxia). ATP export from WT vs. Panx1-/-erythrocytes (RBC) was determined ex vivo via tonometer experimentation across progressive deoxygenation. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) was similar in Panx1-/- (n = 6) and WT (n = 6) mice in normoxia, but the decrease in MAP in hypoxia seen in WT was attenuated in Panx1-/- mice (-16 ± 9% vs. -2 ± 8%; P < 0.05). Hindlimb blood flow (HBF) was significantly lower in Panx1-/- (n = 6) vs. WT (n = 6) basally, and increased in WT but not Panx1-/- mice during hypoxia (8 ± 6% vs. -10 ± 13%; P < 0.05). Estimation of hindlimb vascular conductance using data from the MAP and HBF experiments showed an average response of 28% for WT vs. -9% for Panx1-/- mice. Mean venous plasma ATP during hypoxia was 57% lower in Panx1-/- (n = 6) vs. WT mice (n = 6; P < 0.05). Mean hypoxia-induced ATP export from RBCs from Panx1-/- mice (n = 8) was 82% lower than that from WT (n = 8; P < 0.05). Panx1 channels participate in hemodynamic responses consistent with hypoxic vasodilation by regulating hypoxia-sensitive extracellular ATP levels in blood.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Export of vasodilator ATP from red blood cells requires pannexin 1. Blood plasma ATP elevations in response to hypoxia in mice require pannexin 1. Hemodynamic responses to hypoxia are accompanied by increased plasma ATP in mice in vivo and require pannexin 1.
Keywords: blood flow; erythrocyte; hypoxia; pannexin; vasodilation.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Possible roles for ATP release from RBCs exclude the cAMP-mediated Panx1 pathway.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Dec 1;313(6):C593-C603. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00178.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28855161 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexin 1: a novel regulator of acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Aug 24;118(11):2535-2547. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab326. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 34668529 Free PMC article.
-
Mice Lacking Pannexin 1 Release ATP and Respond Normally to All Taste Qualities.Chem Senses. 2015 Sep;40(7):461-7. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjv034. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Chem Senses. 2015. PMID: 26136251 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Pannexin-1 channel activity.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Jun;43(3):502-7. doi: 10.1042/BST20150042. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 26009198 Review.
-
Emerging concepts regarding pannexin 1 in the vasculature.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Jun;43(3):495-501. doi: 10.1042/BST20150045. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 26009197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Pannexin 1 in the Human Kidney during Embryonal, Early Fetal and Postnatal Development and Its Prognostic Significance in Diabetic Nephropathy.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 20;10(5):944. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10050944. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625681 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexin-1 channel opening is critical for COVID-19 pathogenesis.iScience. 2021 Dec 17;24(12):103478. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103478. Epub 2021 Nov 19. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34841222 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Regulatory Roles of Pannexin 1 in the Pathogenesis and Recovery of Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Aug 25;18:4277-4292. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S532405. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40895608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regadenoson for the treatment of COVID-19: A five case clinical series and mouse studies.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 11;18(8):e0288920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288920. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37566593 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexin1 channels-a potential therapeutic target in inflammation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 9;10:1020826. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1020826. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36438559 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

