Association of digoxin with mortality in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease: A population-based cohort study
- PMID: 33449946
- PMCID: PMC7810292
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245620
Association of digoxin with mortality in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease: A population-based cohort study
Abstract
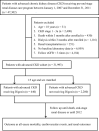
Digoxin is commonly prescribed for heart failure and atrial fibrillation, but there is limited data on its safety in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). We conducted a population-based cohort study using the pre-end stage renal disease (ESRD) care program registry and the National Health Insurance Research Database in Taiwan. Of advanced CKD patient cohort (N = 31,933), we identified the digoxin user group (N = 400) matched with age and sex non-user group (N = 2,220). Multivariable Cox proportional hazards and sub-distribution hazards models were used to evaluate the association between digoxin use and the risk of death, cardiovascular events (acute coronary syndrome, ischemic stroke, or hemorrhagic stroke) and renal outcomes (ESRD, rapid decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate-eGFR, or acute kidney injury). Results showed that all-cause mortality was higher in the digoxin user group than in the non-user group, after adjusting for covariates (adjusted hazard ratio, aHR 1.63; 95% CI 1.23-2.17). The risk for acute coronary syndrome (sub-distribution hazard ratio, sHR 1.18; 95% CI 0.75-1.86), ischemic stroke (sHR 1.42; 95% CI 0.85-2.37), and rapid eGFR decline (sHR 1.00 95% CI 0.78-1.27) was not significantly different between two groups. In conclusion, our study demonstrated that digoxin use was associated with increased mortality, but not cardiovascular events or renal function decline in advanced CKD patients. This finding warns the safety of prescribing digoxin in this population. Future prospective studies are needed to overcome the limitations of cohort study design.
Conflict of interest statement
Co-author Ping-Hsun Wu is a fellow of PLOS ONE Editorial Board Members. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
References
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37(27):2129–200. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous