Targeting pan-essential genes in cancer: Challenges and opportunities
- PMID: 33450197
- PMCID: PMC8157671
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.12.008
Targeting pan-essential genes in cancer: Challenges and opportunities
Abstract
Despite remarkable successes in the clinic, cancer targeted therapy development remains challenging and the failure rate is disappointingly high. This problem is partly due to the misapplication of the targeted therapy paradigm to therapeutics targeting pan-essential genes, which can result in therapeutics whereby efficacy is attenuated by dose-limiting toxicity. Here we summarize the key features of successful chemotherapy and targeted therapy agents, and use case studies to outline recurrent challenges to drug development efforts targeting pan-essential genes. Finally, we suggest strategies to avoid previous pitfalls for ongoing and future development of pan-essential therapeutics.
Keywords: drug development; pan-essential genes; target identification; target validation; targeted therapies.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests W.R.S. is a board or SAB member and holds equity in Ideaya Biosciences, Civetta Therapeutics, and Bluebird bio and has consulted for Array, Astex, Dynamo Therapeutics, Epidarex Capital, Ipsen, PearlRiver Therapeutics, Sanofi, Servier and Syndax Pharmaceuticals, and receives research funding from Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, Merck Pharmaceuticals, Ideaya Biosciences and Ridgeline Discovery. W.R.S. is a co-patent holder on EGFR mutation diagnostic patents. T.I. is an employee and shareholder of Scorpion Therapeutics.
Figures
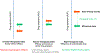
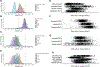
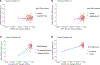
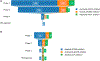
References
-
- Álvarez-Fernández M, and Malumbres M (2020). Mechanisms of sensitivity and resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition. Cancer Cell 37, 514–529. - PubMed
-
- Ando K, Ozaki T, Yamamoto H, Furuya K, Hosoda M, Hayashi S, Fukuzawa M, and Nakagawara A (2004). Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) inhibits p53 function by physical interaction and phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem 279, 25549–25561. - PubMed
-
- Ashton S, Song YH, Nolan J, Cadogan E, Murray J, Odedra R, Foster J, Hall PA, Low S, Taylor P, et al. (2016). Aurora kinase inhibitor nanoparticles target tumors with favorable therapeutic index in vivo. Sci. Transl. Med 8, 325ra17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

