Common Pitfalls in the Management of Patients with Micronutrient Deficiency: Keep in Mind the Stomach
- PMID: 33450823
- PMCID: PMC7828248
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13010208
Common Pitfalls in the Management of Patients with Micronutrient Deficiency: Keep in Mind the Stomach
Abstract
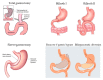
Micronutrient deficiencies are relatively common, in particular iron and cobalamin deficiency, and may potentially lead to life-threatening clinical consequences when not promptly recognized and treated, especially in elderly patients. The stomach plays an important role in the homeostasis of some important hematopoietic micronutrients like iron and cobalamin, and probably in others equally important such as ascorbic acid, calcium, and magnesium. A key role is played by the corpus oxyntic mucosa composed of parietal cells whose main function is gastric acid secretion and intrinsic factor production. Gastric acid secretion is necessary for the digestion and absorption of cobalamin and the absorption of iron, calcium, and probably magnesium, and is also essential for the absorption, secretion, and activation of ascorbic acid. Several pathological conditions such as Helicobacter pylori-related gastritis, corpus atrophic gastritis, as well as antisecretory drugs, and gastric surgery may interfere with the normal functioning of gastric oxyntic mucosa and micronutrients homeostasis. Investigation of the stomach by gastroscopy plus biopsies should always be considered in the management of patients with micronutrient deficiencies. The current review focuses on the physiological and pathophysiological aspects of gastric acid secretion and the role of the stomach in iron, cobalamin, calcium, and magnesium deficiency and ascorbate homeostasis.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; anemia; ascorbic acid; atrophic gastritis; autoimmune gastritis; bariatric surgery; calcium deficiency; cobalamin deficiency; iron deficiency; magnesium deficiency; micronutrients; pernicious anemia; proton pump inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Biebinger R., Hurrell R.F. 3—Vitamin and mineral fortification of foods. In: Ottaway P.B., editor. Food Fortification and Supplementation. Woodhead Publishing; Cambridge, UK: 2008. pp. 27–40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

