Could Chronic Idiopatic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction Be Related to Viral Infections?
- PMID: 33450988
- PMCID: PMC7828444
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10020268
Could Chronic Idiopatic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction Be Related to Viral Infections?
Abstract
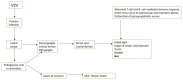
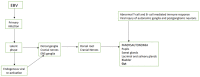
Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction (CIIPO) is a disease characterized by symptoms and signs of small bowel obstruction in the absence of displayable mechanical obstruction. Due to the known neuropathic capacity of several viruses, and their localization in the intestine, it has been hypothesized that such viruses could be involved in the pathogenesis of CIIPO. The most frequently involved viruses are John Cunningham virus, Herpesviridae, Flaviviruses, Epstein-Barr virus and Citomegalovirus. Therefore, the present narrative review aims to sum up some new perspectives in the etiology and pathophysiology of CIIPO.
Keywords: chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction; gastrointestinal motility disorders; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stanghellini V., Cogliandro R.F., De Giorgio R., Barbara G., Morselli-Labate A.M., Cogliandro L., Corinaldesi R. Natural History of Chronic Idiopathic Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction in Adults: A Single Center Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005;3:449–458. doi: 10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00675-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources