Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Nephrotoxicity in Kidney Impairment: The Physio-Pathological Conditions for the Perfect Murder
- PMID: 33450989
- PMCID: PMC7828445
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10020271
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Nephrotoxicity in Kidney Impairment: The Physio-Pathological Conditions for the Perfect Murder
Abstract
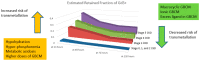
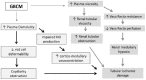
Gadolinium-based contrast media (GBCM) toxicity in patients with kidney disease is a concern for the possible development of systemic nephrogenic fibrosis and possible renal complications. This review focuses on the pathological mechanisms underlying the potential kidney toxicity of gadolinium. Gadolinium, as a free compound (Gd3+), is highly toxic in humans because it competes with divalent calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions, interfering in some relevant biologic processes. Its toxicity is blunted by the complexing of Gd3+ with a carrier, allowing its use in magnetic resonance imaging. The binding reaction between gadolinium and a carrier is thermodynamically reversible. Consequently, under some conditions, gadolinium can be released in the interstitial space as a free Gd3+ compound with the possibility of toxicity. Other metals such as iron, copper, and calcium can interfere with the binding between gadolinium and its carrier because they compete for the same binding site. This process is known as transmetallation. In patients with kidney impairment, conditions such as low clearance of the Gd-carrier complex, acid-base derangements, and high serum phosphorous can increase the presence of free Gd3+, leading to a higher risk for toxicity.
Keywords: gadolinium-based contrast media; kidney damage; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Deray G., Rouviere O., Bacigalupo L., Maes B., Hannedouche T., Vrtovsnik F., Rigothier C., Billiouw J.M., Campioni P., Ferreiros J., et al. Safety of Meglumine Gadoterate (Gd-DOTA)-enhanced MRI Compared to Unenhanced MRI in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (RESCUE Study) Eur. Radiol. 2013;23:1250–1259. doi: 10.1007/s00330-012-2705-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

