Biological Sound vs. Anthropogenic Noise: Assessment of Behavioural Changes in Scyliorhinus canicula Exposed to Boats Noise
- PMID: 33451005
- PMCID: PMC7828510
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11010174
Biological Sound vs. Anthropogenic Noise: Assessment of Behavioural Changes in Scyliorhinus canicula Exposed to Boats Noise
Abstract
Despite the growing interest in human-made noise effects on marine wildlife, few studies have investigated the potential role of underwater noise on elasmobranch species. In this study, twelve specimens of small-spotted catshark (Scyliorhinus canicula) were exposed to biological and anthropogenic sounds in order to assess their behavioural changes in response to prey acoustic stimuli and to different amplitude levels of shipping noise. The sharks, individually held in aquariums, were exposed to four experimental acoustic conditions characterized by different spectral (Hz) components and amplitude (dB re 1 µPa) levels. The swimming behaviour and spatial distribution of sharks were observed. The results highlighted significant differences in swimming time and in the spatial use of the aquarium among the experimental conditions. When the amplitude levels of biological sources were higher than those of anthropogenic sources, the sharks' swimming behaviour was concentrated in the bottom sections of the aquarium; when the amplitude levels of anthropogenic sources were higher than biological ones, the specimens increased the time spent swimming. Moreover, their spatial distribution highlighted a tendency to occupy the least noisy sections of the aquarium. In conclusion, this study highlighted that anthropogenic noise is able to affect behaviour of catshark specimens and the impact depends on acoustic amplitude levels.
Keywords: anthropogenic noise; biological sounds; signal/noise ratio; small-spotted catshark.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
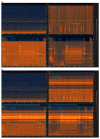
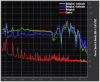



References
-
- Buscaino G., Gavio A., Galvan D., Filiciotto F., Maccarrone V., de Vincenzi G., Mazzola S., Orensanz J. Acoustic signals and behaviour of Ovalipes trimaculatus in the context of reproduction. Aquat. Biol. 2015;24:61–73. doi: 10.3354/ab00636. - DOI
-
- Coquereau L., Grall J., Clavier J., Jolivet A., Chauvaud L. Acoustic behaviours of large crustaceans in NE Atlantic coastal habitats. Aquat. Biol. 2016;25:151–163. doi: 10.3354/ab00665. - DOI
-
- de Vincenzi G., Parisi I., Torri M., Papale E., Mazzola S., Nuth C., Buscaino G. Influence of environmental parameters on the use and spatiotemporal distribution of the vocalizations of bearded seals (Erignathus barbatus) in Kongsfjorden, Spitsbergen. Polar Biol. 2019;42:1241–1254. doi: 10.1007/s00300-019-02514-3. - DOI
-
- de Vincenzi G., Filiciotto F., Maccarrone V., Mazzola S., Buscaino G. Behavioural responses of the European spiny lobster, Palinurus elephas (Fabricius, 1787), to conspecific and synthetic sounds. Crustaceana. 2015;88:523–540. doi: 10.1163/15685403-00003430. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

