Synthesis of D-Limonene Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles with Enhanced Antimicrobial Properties for Potential Application in Food Packaging
- PMID: 33451168
- PMCID: PMC7828745
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11010191
Synthesis of D-Limonene Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles with Enhanced Antimicrobial Properties for Potential Application in Food Packaging
Abstract
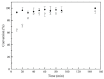
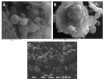
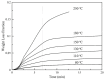
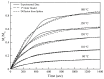
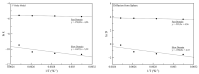
Mini-emulsion polymerization was applied for the synthesis of cross-linked polymeric nanoparticles comprised of methyl methacrylate (MMA) and Triethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate (TEGDMA) copolymers, used as matrix-carriers for hosting D-limonene. D-limonene was selected as a model essential oil, well known for its pleasant odor and its enhanced antimicrobial properties. The synthesized particles were assessed for their morphology and geometric characteristics by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), which revealed the formation of particles with mean diameters at the nanoscale (D[3,2] = 0.135 μm), with a spherical shape, while the dried particles formed larger clusters of several microns (D[3,2] = 80.69 μm). The percentage of the loaded D-limonene was quantified by Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), complemented by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry analysis coupled with a pyrolysis unit (Py/GC-MS). The results showed that the volatiles emitted by the nanoparticles were composed mainly of D-limonene (10% w/w of dry particles). Particles subjected to higher temperatures tended to decompose. The mechanism that governs the release of D-limonene from the as-synthesized particles was studied by fitting mathematical models to the release data obtained by isothermal TGA analysis of the dry particles subjected to accelerated conditions. The analysis revealed a two-stage release of the volatiles, one governed by D-limonene release and the other governed by TEGDMA release. Finally, the antimicrobial potency of the D-limonene-loaded particles was demonstrated, indicating the successful synthesis of polymeric nanoparticles loaded with D-limonene, owing to enhanced antimicrobial properties. The overall performance of these nanoparticles renders them a promising candidate material for the formation of self-sterilized surfaces with enhanced antimicrobial activity and potential application in food packaging.
Keywords: D-limonene; antimicrobial properties; cross-linking; essential oils; mini-emulsion polymerization; nanoparticles; volatile release.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The Formation of Self-Assembled Nanoparticles Loaded with Doxorubicin and d-Limonene for Cancer Therapy.ACS Omega. 2022 Nov 13;7(46):42096-42104. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04238. eCollection 2022 Nov 22. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36440142 Free PMC article.
-
Development and characterization of electrosprayed Alyssum homolocarpum seed gum nanoparticles for encapsulation of d-limonene.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Mar 15;490:562-575. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.11.067. Epub 2016 Nov 21. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 27923141
-
Calcium phosphate nanoparticles functionalized with a dimethacrylate monomer.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014 Dec;45:122-6. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2014.08.066. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014. PMID: 25491810
-
Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antiseptic activity and toxicity mechanism.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Nov;249:37-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.07.033. Epub 2017 Aug 26. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 28923702 Review.
-
Nanodelivery systems for d-limonene; techniques and applications.Food Chem. 2022 Aug 1;384:132479. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132479. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35413770 Review.
Cited by
-
Encapsulation of Volatile Monoterpene Fragrances in Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles and Potential Application in Fruit Preservation.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;13(1):104. doi: 10.3390/nano13010104. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616014 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Bio-Composites with Enhanced Antioxidant Activity Based on Poly(lactic acid) with Thymol, Carvacrol, Limonene, or Cinnamaldehyde for Active Food Packaging.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Oct 23;13(21):3652. doi: 10.3390/polym13213652. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771206 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Promoting Properties and Potential Application in the Food Industry of Citrus medica L. and Citrus × clementina Hort. Ex Tan. Essential Oils and Their Main Constituents.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 21;12(5):991. doi: 10.3390/plants12050991. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36903853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles-Attractive Carriers of Antimicrobial Essential Oils.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jan 14;11(1):108. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010108. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrophysiological and Behavioral Responses of Batocera horsfieldi Hope to Volatiles from Pistacia chinensis Bunge.Insects. 2023 Nov 27;14(12):911. doi: 10.3390/insects14120911. Insects. 2023. PMID: 38132585 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Méndez-Vilas A. Microbial Pathogens and Strategies for Combating Them: Science, Technology and Education. Formatex Research Center; Norristown, PA, USA: 2013.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

